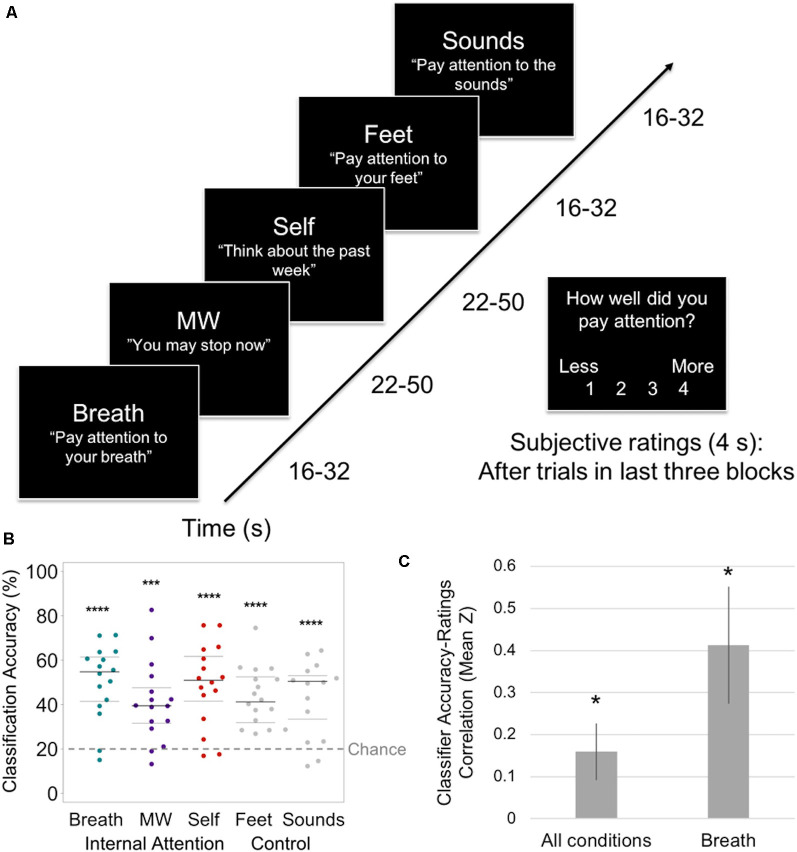
Figure 2.
EMBODY Step 1: classifier training of internal mental states. (A) Internal Attention (IA) task. With eyes closed, participants were directed via 2-s auditory instructions to pay attention to five internal mental states for brief periods (16–50 s). The IA task-directed attention to three mental states relevant for breath meditation [Breath, mind wandering (MW), and Self], and two control mental states [attention to the Feet (another area of the body) and ambient MRI Sounds (consistent external distractor)]. The example auditory instructions are displayed in quotes. MW was induced by instructing participants to stop paying attention and let their minds attend to whatever they wanted. Conditions were randomized over six IA blocks in four orders, with 72 s of data collected from each condition in each block (total 432 s/condition). For the last half of IA task trials, subjective ratings of attention were collected after each trial (except MW) using a button box (1 = less, 4 = more). (B) From the IA task, the prediction accuracy of the classifier for identifying internal states of attending to the Breath, MW, and Self, and control conditions of attending to the Feet and Sounds. Beeswarm plots present each data point, the median (bold black line), and ±25th percentile range (gray lines) of the mean prediction accuracy for all data in each condition (n = 432) across all subjects. Statistical significance was determined by a one-sample two-sided t-test against theoretical chance-level for classification of five categories (20%, denoted by a dashed line). ***t(15) = 4.65, p < 0.001, ****ts15 > 5.67, ps < 0.0001. (C) Mean z-scores representing the within-subject correlation between trial-level classifier training accuracy and subjective ratings of attention (administered during the last half of IA task trials) for all conditions (except MW) and breath trials only. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05.