Figure 6. Pharmacological inhibition of PHGDH attenuates brain metastasis.
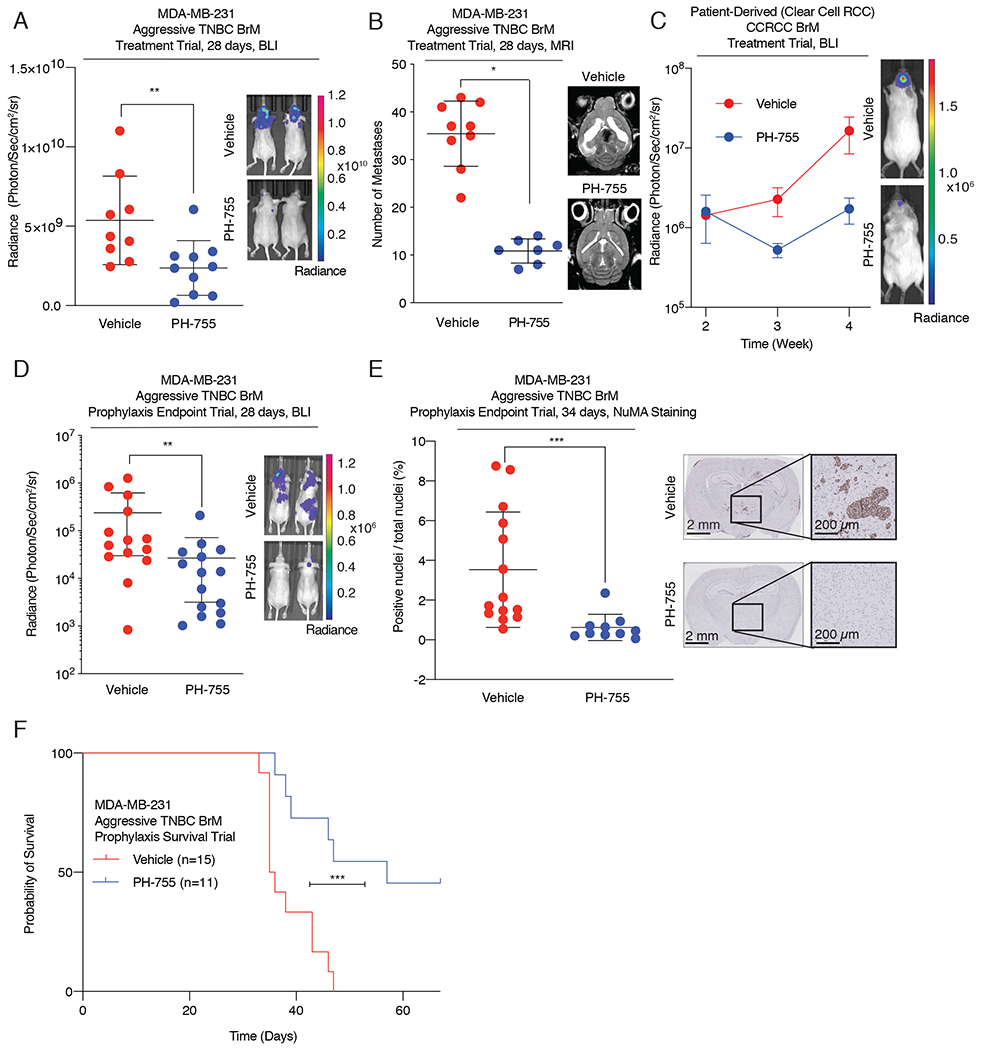
(A) Radiance, measured at 28 days post intracardiac injection, of aggressive TNBC BrM-bearing mice treated with vehicle or 300 mg/kg of PH-755 twice daily. Treatment began 1.5 weeks after the initial introduction of cancer cells into mice.
(B) Quantification of brain metastatic lesions by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) from mice treated with vehicle control or 300mg/kg of PH-755 twice daily.
(C) Radiance of RCC BrM PDX brain metastasis-bearing mice treated with vehicle or 300 mg/kg of PH-755 twice daily. Treatment began 2 weeks after the initial introduction of cancer cells into mice. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM).
(D) Radiance, measured at 28 days post intracardiac injection, of aggressive TNBC BrM-bearing mice treated prophylactically with vehicle or 300 mg/kg PH-755 twice daily.
(E) Quantitation by IHC of human Nuclear Mitotic Apparatus (NuMA)-positive nuclei relative to total nuclei count, indicating the burden of brain metastases, from mice treated prophylactically with vehicle or PH-755. Tissue was harvested 34 days post injection
(F) Kaplan-Meier plot showing overall survival of mice treated prophylactically with vehicle or 300 mg/kg PH-755 twice daily.
