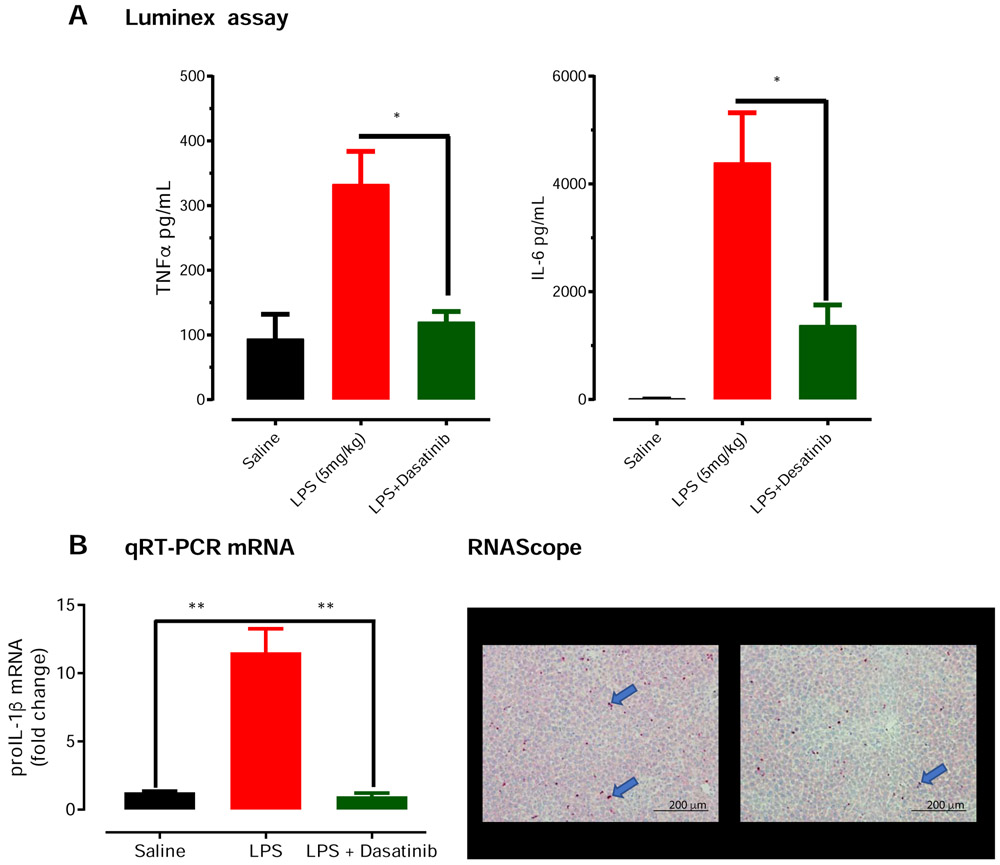
Fig 7. Co-treatment with dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, protects against LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were randomly separated into 3 groups (n =3). The control group received only saline, the LPS group received 1 dose of LPS at 5mg/kg via subcutaneous administration, and the third group received 1 dose of LPS and 4 doses of dasatinib (10 mg/kg) at the indicated time points. (A) Luminex assay revealed that dasatinib treatment reduced LPS-induced TNF-α and IL-6 proinflammatory cytokine induction in the plasma to near control levels at 1 hour post-LPS treatment. (B). Quantitative PCR and RNA scope. Our qRT-PCR revealed dasatinib significantly reduced transcripts levels of pro-IL-1β in liver tissue (B). Finally, representative images from RNAscope assay probing for pro-IL-1β transcripts (blue arrows) found reduced pro-IL-1β transcripts in liver sections of dasatinib-treated mice Significant differences between groups indicated by *, P ≤ 0.05. Scale bar: 200 μm.