Figure 5. FOXO1 Inhibition Induces HIV Reactivation in the Absence of NF-kB Recruitment via ATF4 and NFAT.
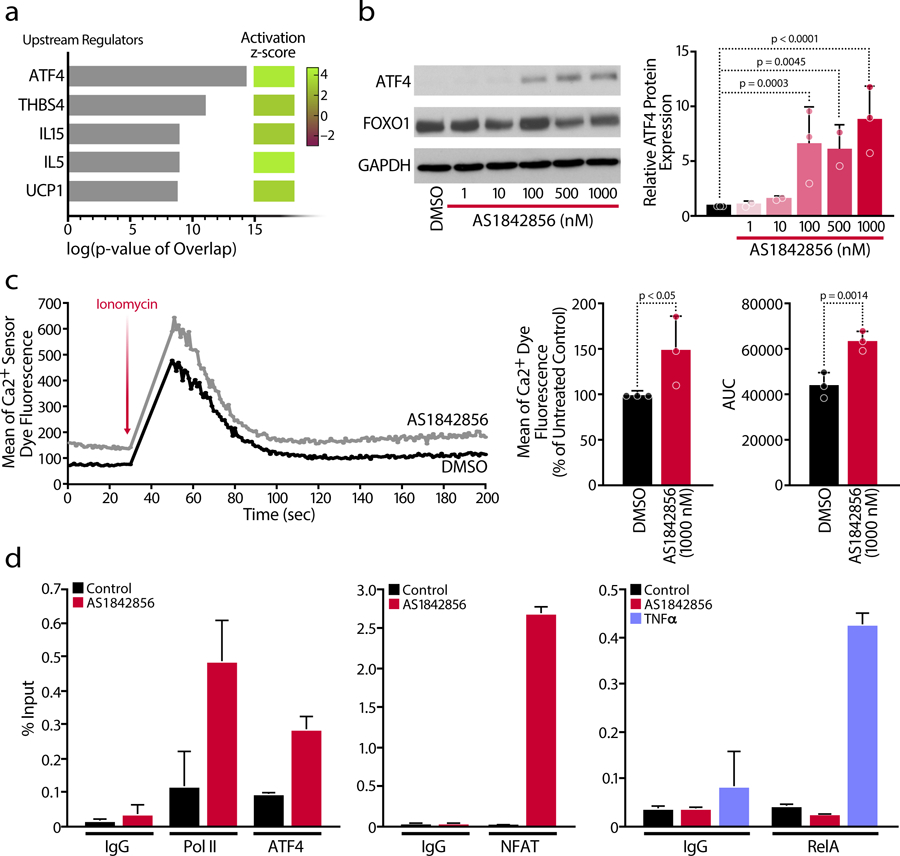
a, Analysis of the five top upstream regulators and table with their activation z-scores according to the RNA-Seq data. b, Representative blot of protein expression of the transcription factors ATF4 and FOXO1 (left) and densitometry analysis of ATF4 protein expression (right) was performed from n=3 individual donors. Data are mean ± SD. c, Representative plot of intracellular calcium-flux kinetics in primary CD4 T cells in the presence or absence of AS1842856 (100 nM). Cells were stained with a membrane permeable calcium sensor dye in PBS and stimulated by adding Ionomycin after 30 seconds resulting in an increase of fluorescence indicating a calcium mobilization from the ER. The mean of the calcium sensor dye fluorescence at basal condition (before Ionomycin stimulation, 0–30 sec) and the parameter Area Under the Curve (AUC) relative to the calcium flux were calculated. Data are represented as mean ± SD of n=3 independent experiments. d, Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays with antibodies against Pol II, ATF4, RelA, NFAT and IgG control at the HIV LTR, followed by qPCR using primers specific for HIV-1 LTR Nuc0 or Nuc1. Chromatin was prepared from J-Lat A2 and 5A8 cells, in which the LTR was stimulated by 1,000 nM AS1842856 treatment, 10 ng/mL TNFα or which were left untreated/DMSO. Representative experiment of n=3 independent biological experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SD of n=3 independent technical replicates.
