Figure 1. Wnt/planar cell polarity is a conserved axon guidance signaling system.
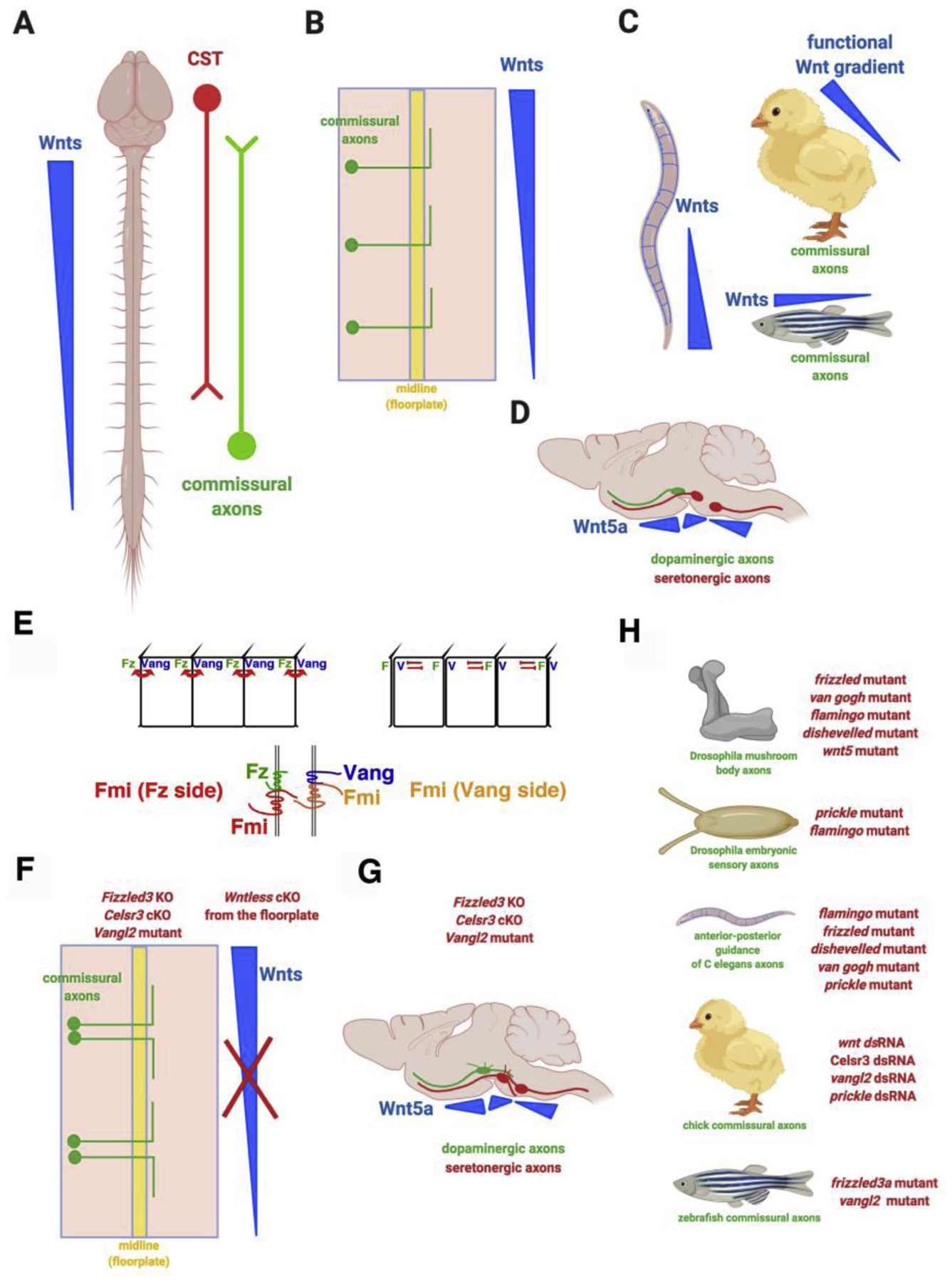
A. Wnts are guidance cues for anterior-posterior (rostral-caudal) pathfinding of ascending and descending axons in rodent spinal cord. CST: corticospinal tract.
B. Ascending spinal cord commissural axons turn anteriorly after they cross the midline, the floor plate.
C. Wnts are anterior-posterior axon guidance cues in C elegans. Wnts guidance spinal cord commissural axons to turn anteriorly after midline crossing in chick and zebrafish.
D. Wnt gradients guide the anterior-posterior growth of dopaminergic and serotonergic axons in the brainstem.
E. Schematics of the distribution of and the interactions among the planar cell polarity signaling components within the same epithelial cell or between the neighboring cells: Fmi (Flamingo or Celsr), Fz (Frizzled), Vang (Van Gogh).
F. Spinal cord commissural axons lose directionality along the anterior-posterior axis, turning randomly along the A-P axis after midline crossing in Frizzled3, Ceslr3 and Vangl2 mutants and in floor plate-specific conditional knockout of Wntless, encoding the Wnt cargo receptor required for the secretion of all Wnt proteins
G. Wnt gradients guide the anterior-posterior growth of dopaminergic and serotonergic axons in the brainstem via the planar cell polarity components.
H. PCP components are also required for the guidance of mushroom body axons in Drosophila, sensory axons in Drosophila, mechanosensory axons in C. elegans, chick spinal cord commissural axons and zebrafish spinal cord commissural axons.
