Figure 3. Planar cell polarity and apical-basal polarity signaling are key regulators of glutamatergic synapse formation.
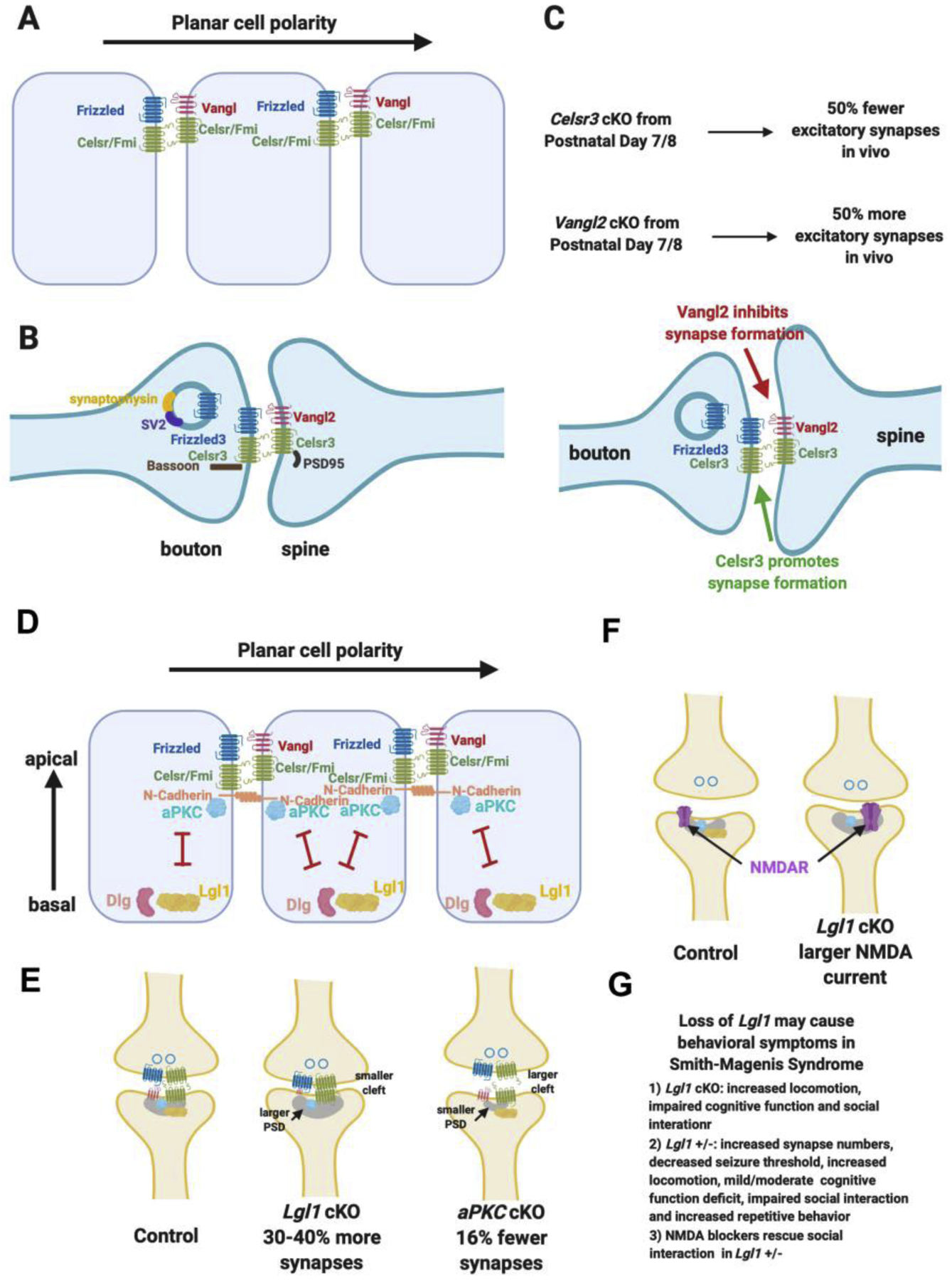
A. Schematics of the asymmetric localization of planar cell polarity components in epithelial cells and the asymmetric intercellular complexes.
B. Planar cell polarity components are localized in the glutamatergic synapse in similar ways as in epithelial polarization signaling and interact with key synaptic proteins.
C. Loss of Celsr3 (encoding one of the two Celsrs found in glutamatergic synapses) lead to reduction of the formation of 50% of the glutamatergic synapses in vivo when conditionally knocked out from postnatal day 7/8. Loss of Vangl2 lead to a large increase of glutamatergic synapse numbers in vivo.
D. Apical-basal polarity is perpendicular to planar cell polarity and is mediated by the antagonistic interactions and localization of aPKC and Lgl.
E. Lgl1 cKO lead to a large increase of glutamatergic synapse numbers, larger postsynaptic density, smaller synaptic cleft and reduced Vangl2 protein in the synaptosome. aPKC double cKO lead to a decrease of glutamatergic synapse numbers, smaller postsynaptic density and larger synaptic cleft.
F. Lgl1 +/− animals display behavioral deficit mimicking human Smith-Magenis Syndrome and the behavioral deficit can be rescued by NDMAR blockers.
