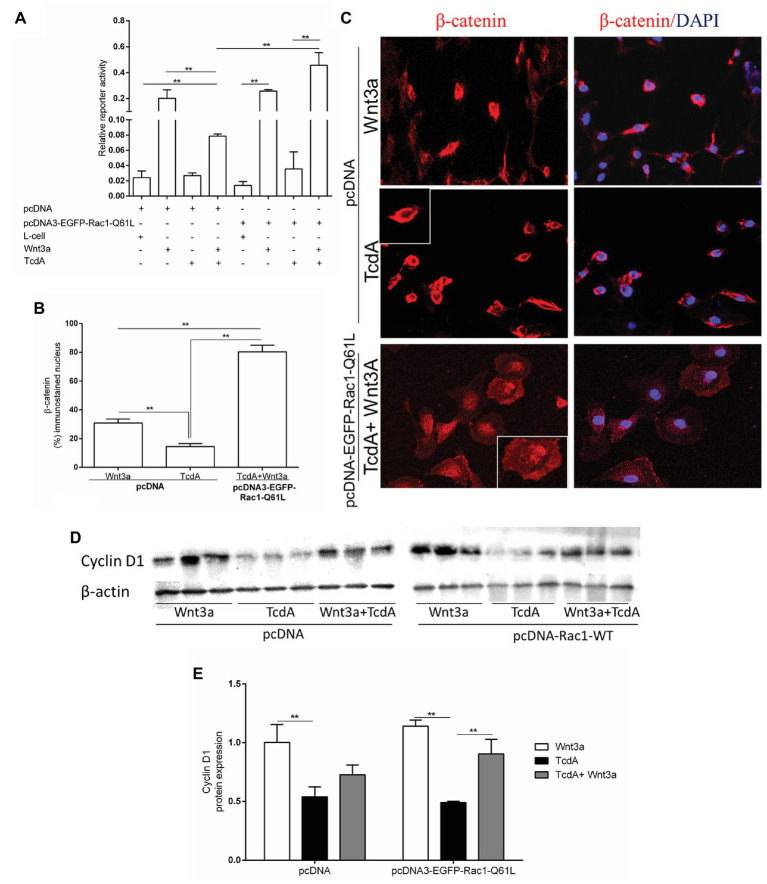
Figure 5.
Upregulation of Rac1 reverses the TcdA inhibitory effect on β-catenin nuclear translocation induced by Wnt3a in intestinal epithelial cells (IEC-6). (A) Relative reporter activity of β-catenin/T cell factor (TCF) signaling in the IEC-6 cells cotransfected with pcDNA (empty vector) or pcDNA3-EGFP-Rac1-Q61L, and TOPflash luciferase reporter constructs followed by incubation with TcdA (50 ng/ml), Wnt3a-conditioned or L-cell medium for 24 h. Renilla luciferase constructs were used as an internal control for transfection efficiency. Bars represent the means ± SEM (n = 5). One-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s test, was used; **p < 0.001. (B) Percentage of cells showing positive β-catenin immunostaining in the nucleus. Data are the means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s test, was used; **p < 0.001. (C) Representative photomicrographs of immunostained β-catenin (red) and DAPI, a nuclear dye (blue), in IEC-6 cells transfected with pcDNA (empty vector) or pcDNA3-EGFP-Rac1-Q61L followed by 24 h incubation with TcdA (50 ng/ml) alone or Wnt3a-conditioned medium (Wnt3a-CM). (D) The WB bands of each group showing cyclin D1 and β-actin (a control protein) protein expression from lysed IEC-6 cells after 24 h of incubation. (E) Analysis of the relative band densities of cyclin D1 normalized to β-actin. Bars represent the means ± SEM (n = 5). One-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s test, was used; **p < 0.001.