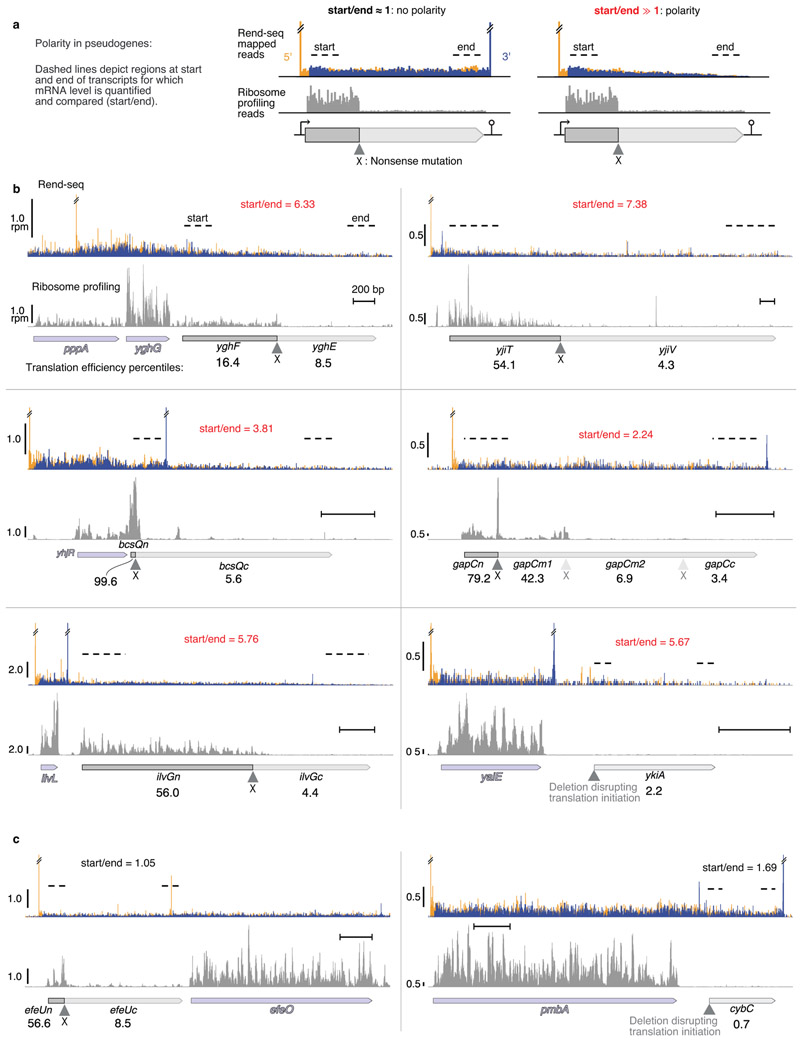
Extended Data Figure 8. Most expressed pseudogenes with interrupted translation in E. coli show polarity.
Similar to Extended Data Figure 7. Expressed pseudogenes endogenously present in the extant genome were used as additional independent experiments to assess the prevalence of Rho-mediated nonsense polarity in E. coli in situations of obligately uncoupled transcription and translation. Concomitant Rend-seq (mapping operon architecture) and ribosome profiling (monitoring translation) provides stringent data to determine translational status and transcript integrity on mRNAs. a, Schematic of analysis: for expressed pseudogenes (see Methods for selection criteria) with translation disruption, polarity was assessed by comparing the mRNA read density at start and end of transcription unit, with large changes (start/end⨠1) indicative of polarity. b, Rend-seq and ribosome profiling data for the identified expressed pseudogene with evidence of polarity. Each subpanel corresponds to a pseudogene region. Top traces correspond to Rend-seq data (orange and blue signal correspond to summed 5’-mapped reads and 3’-mapped reads, peak shadows removed, see35 for details on data processing). Orange peaks and blue peaks mark 5’ and 3’ boundaries of transcripts. Double line breaks (//) indicate truncated Rend-seq signal at peaks. Bottom traces show ribosome profiling data. Translation efficiency (ribosome profiling rpkm/Rend-seq rpkm) percentiles for each pseudogene sub-region (before and after translation disruption) are shown. Horizontal size marker provides positional scale (200 bp) on each subpanel. Light blue arrows correspond to nearby intact genes. rpm: reads per million. Regions used to assess start to end decrease in RNA levels are marked by dashed lines. mRNA levels fold-changes (start/end) are shown. The gapC region showed sequential translation disruptions secondary frames, shown as a pale ▲ and X. c, same as b, but for the two cases with no evidence of polarity. The translation disruptions mutation in ykiA and cybC are deletion of the beginning of ORFs. See Methods, Fig. 3b and Supplementary Data 3 for details.