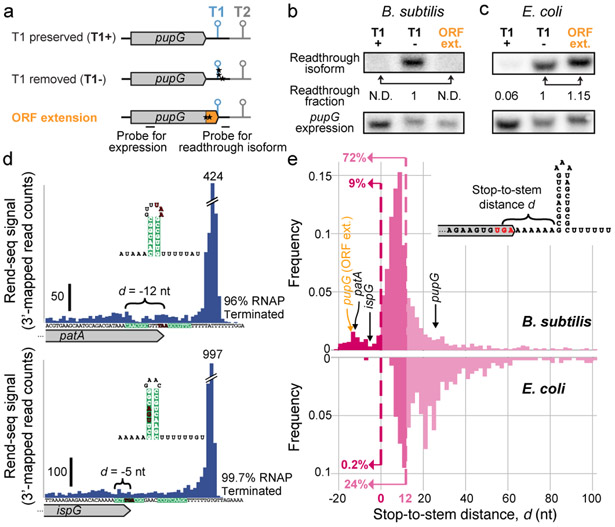
Fig. 2: Lack of translational control on transcription.
a, Schematics of ORF-extension construct and controls for pupG (80th percentile in translation efficiency). T1: pupG terminator (99.97% termination efficiency), T2: sodA terminator (99.9% termination efficiency). Stars indicate mutations. The stop-to-stem distances d for the native and extended constructs are 26 nt and minus 14 nt respectively. b-c, Northern blots against readthrough isoforms (top) and control for pupG expression (bottom) for constructs indicated in a. N.D.: not detected. For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1. Northern blotting was performed twice for B. subtilis (biological replicates) and once for E. coli. Results for both species were independently confirmed (biological replicates) by qRT-PCR (Methods). d, Examples of terminator stem-loops overlapping with stop codons (patA d=−12 nt, ispG d=−5 nt). Peaks in Rend-seq data show sites of termination. Terminator stems are highlighted. Stop codons are indicated in red. Translation efficiencies for patA and ispG are 63rd and 90th percentiles, respectively, in B. subtilis. e, Genome-wide distribution of stop-to-stem distances d (see inset) for high-confidence intrinsic terminators in B. subtilis (top, n=1228) and E. coli (bottom, n=409). ORF-overlapping terminators (d≤0) are in dark magenta, and ribosome-overlapping terminators (d≤12 nt) are in medium and dark magenta, with respective fraction of terminators indicated. See also Extended Data Fig. 5, Supplementary Data 2.