Fig. 5.
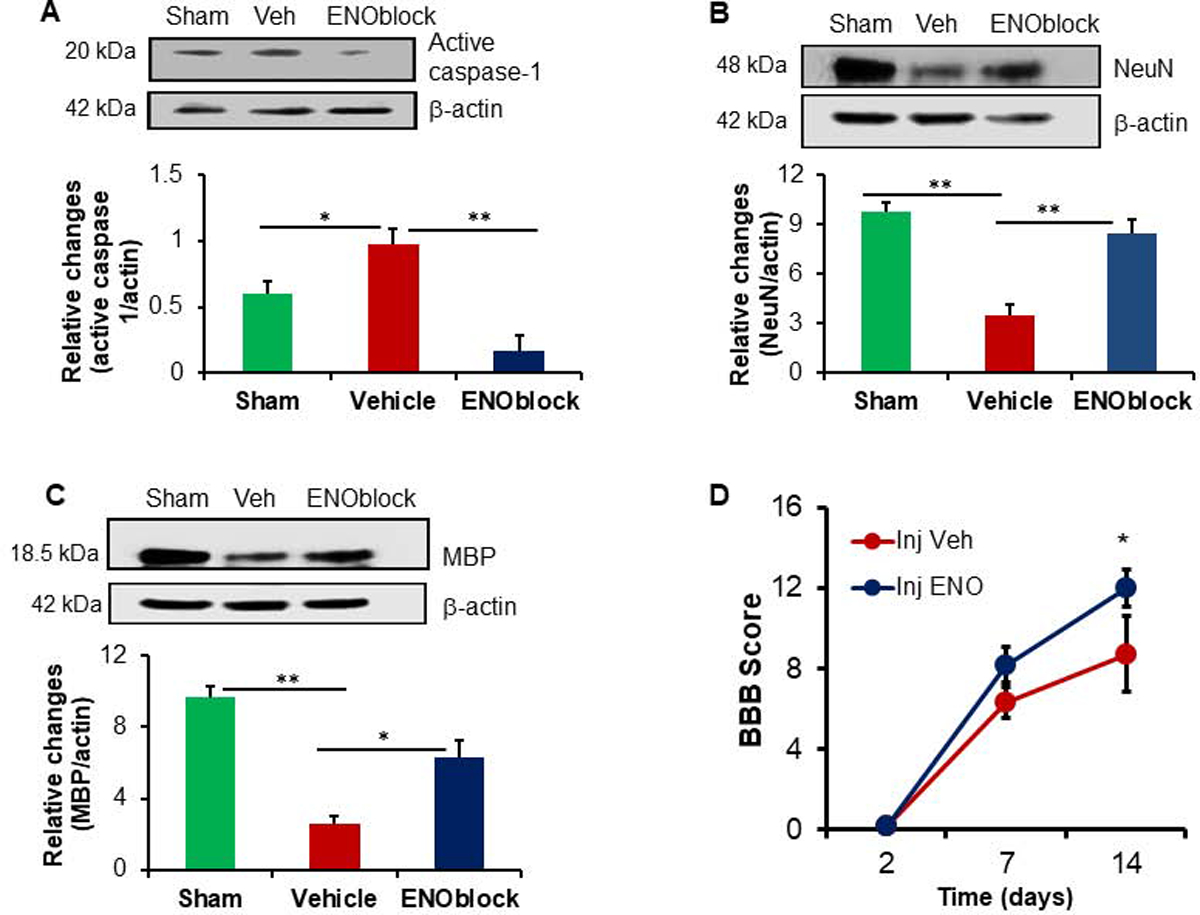
ENOblock treatment decreases active caspase-1, increases NeuN and MBP, and improves functional outcome in SCI rats. Spinal cord samples from sham, vehicle and ENOblock treated animals were subjected to western blotting for active forms of caspase-1 (A), NeuN (B), and MBP (C) as shown in the upper panels. Densitometric analysis (A, lower panel) showed that active caspase-1 was elevated in injured rats, which was significantly downregulated following ENOblock treatment. By contrast, NeuN (B, lower panel) and MBP (C, lower panel) proteins were significantly downregulated after SCI, and that ENOblock treatment protected these proteins in SCI rats. (One-way ANOVA, *p<0.05, **p<0.01; n=3–4). (D) Assessment of BBB scores in the SCI rats. An improved BBB score is found in the ENOblock treated group (Injection + ENOblock), as compared with vehicle treated group (Injection + Vehicle) on Day 14. Sham animals, scored 21 at each time point, are not displayed. Data suggest that there is a significant improvement in functional outcome in ENOblock treated rats following SCI. (One-way ANOVA with Fisher’s post-hoc test, n=5–8, *p<0.05).
