Extended Data Fig. 2. Circular vs amplified non-circular amplification comparisons.
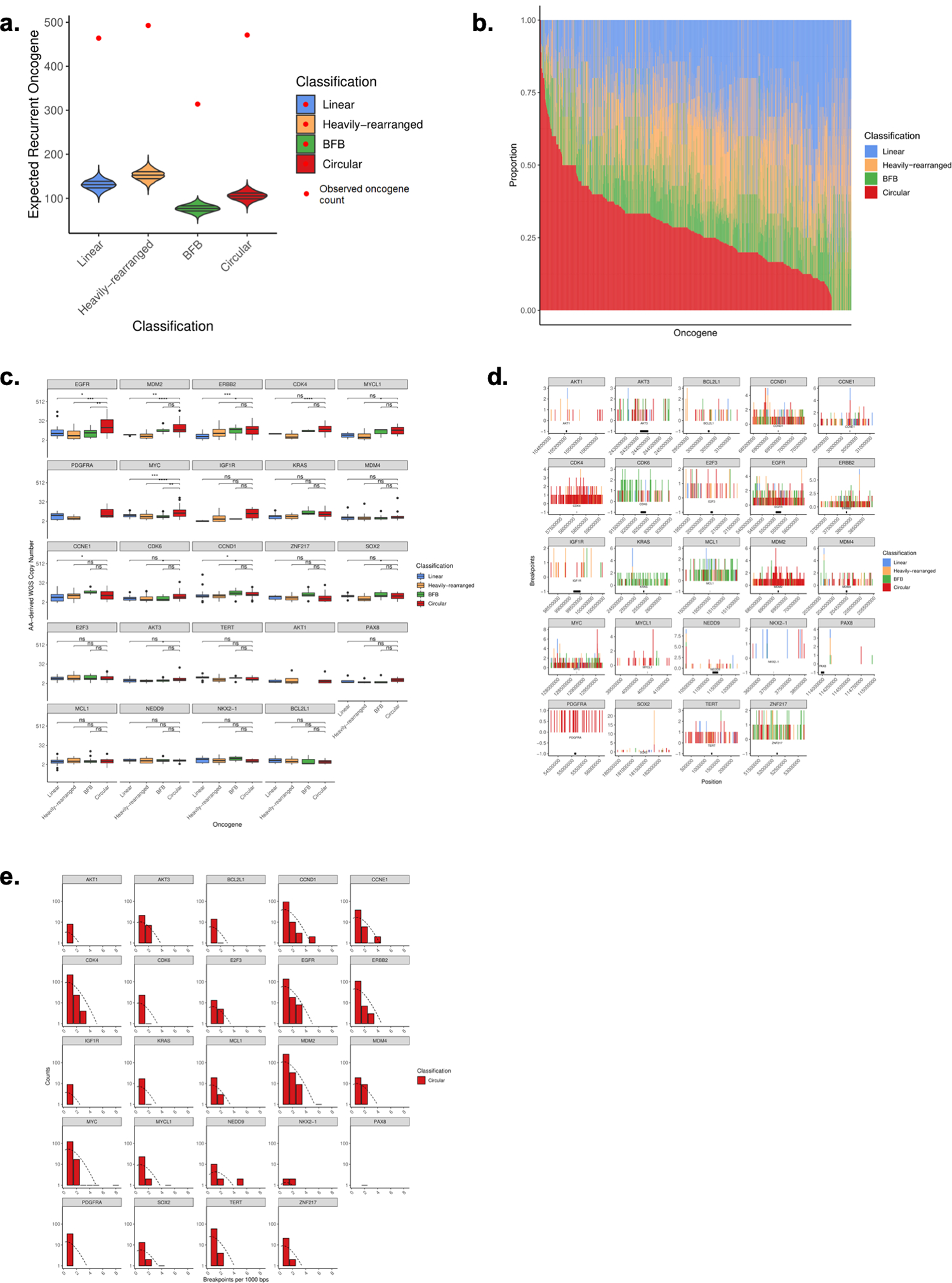
A. 24 recurrently amplified oncogenes significantly overlap circular regions (z-score 37.8), especially compared to amplified non-circular regions (z-scores of 30.4, 29.5, 28.0 for Linear, Heavily-rearranged, and BFB). B. For all oncogenes on amplicons with copy number >= 4 and present in at least 5 samples across the cohort, we show the class distribution of that oncogene. The oncogenes are ordered by proportion on circular amplification. C. For the 24 recurrent oncogenes known to be activated via amplification (Zack et al. Nat Gen. 2013), we report the average copy number for the oncogenes for circular amplification versus amplified-noncircular amplification. D. Breakpoint location across all samples for each recurrently amplified oncogene. We identified all breakpoints from each sample containing the recurrent oncogene on ecDNA and report the total number of breakpoints across this region in 1kb binned windows. E. Distribution of breakpoint locations across all circular samples for each recurrently amplified oncogene. We identified all breakpoints from each sample containing the recurrent oncogene on ecDNA. Shown is the distribution of the number of breakpoints in each bin, which closely follows a Poisson distribution, suggesting that the breakpoints are mostly randomly distributed across the region.
