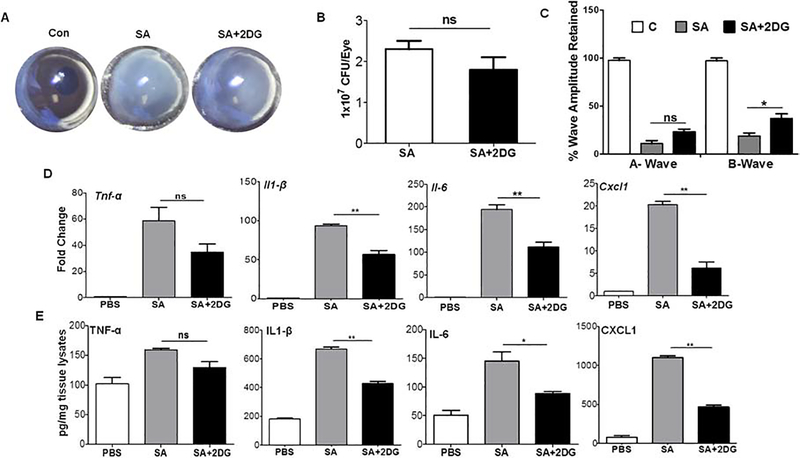
Figure 5. 2DG post-treatment attenuates S. aureus induced intraocular inflammation in mouse eyes.
WT C57BL/6 mice (n=10) eyes were infected with S. aureus and at 6 h post-infection eyes were treated with 2DG (25 μg/eye) by intravitreal injection. 24 h post-2DG treatment eyes were examined and photomicrograph was taken (A). Eyes were enucleated and subjected to bacterial burden estimation by plate count (B). The retinal function was measured using scotopic ERG (C). The retinal tissue was subjected to qPCR for various pro-inflammatory mediators (D). The eye lysates were subjected to ELISA for cytokine/chemokine quantification (E). A one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test was used to determine statistical significance. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ns: not significant. Data represent mean ± SD.