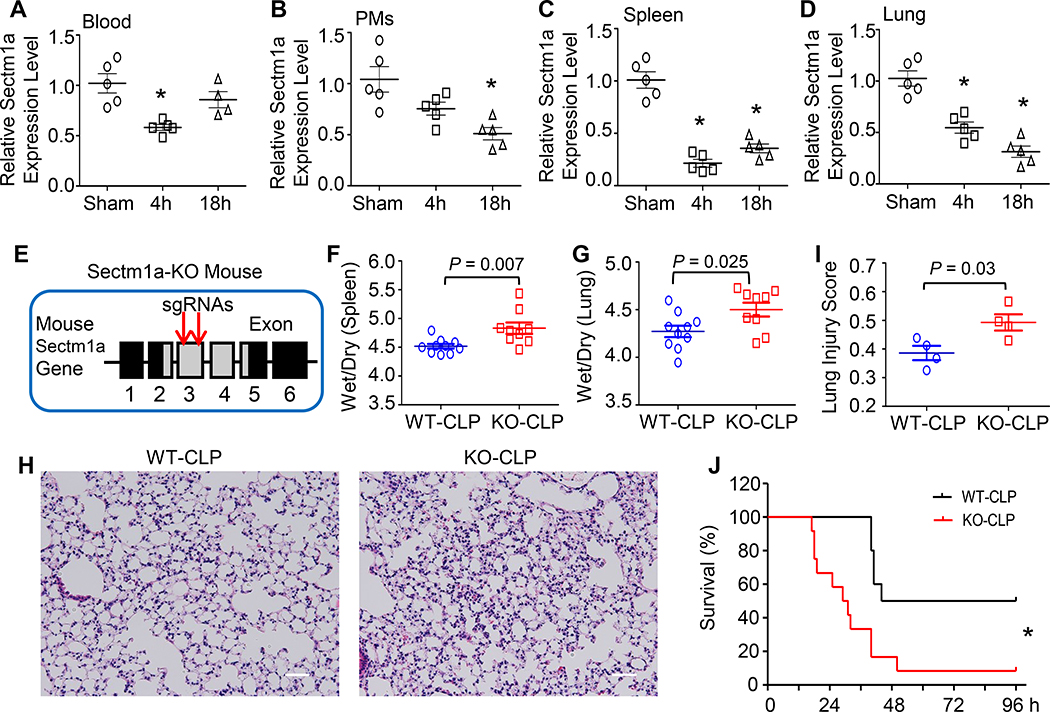
Figure 1. Sectm1a depletion aggravates polymicrobial sepsis-induced multi-organ damage and mortality.
(A-D) Expression levels of Sectm1a were determined in (A) blood, (B) peritoneal macrophages (PMs), (C) spleen and (D) lung collected from WT mice at indicated time points after CLP surgery (*, P < 0.05; n = 5). (E) Two gRNAs targeting to Exon3 of Sectm1a gene were selected to generate Sectm1a-KO mouse model, detailed in Ref. 19. (F-G) At 24 h post-CLP, wet weight to dry weight ratios of spleen (F) and lung (G) were quantified (n = 9–10). (H) Representative images of lung section with H&E staining at 24 h after CLP surgery were shown at ×200 original magnification. Scale bars, 50 μm. (I) Lung injury scores were assessed as described in Materials and Methods (n = 4). (J) WT (n=10) and Sectm1a-KO mice (n=12) were monitored for survival up to 96 h after CLP surgery and analyzed by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Data are representative of two (A-D, H-J) or three (F-G) independent experiments. Except survival test, all other results are presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by one-way ANOVA or student’s t test.