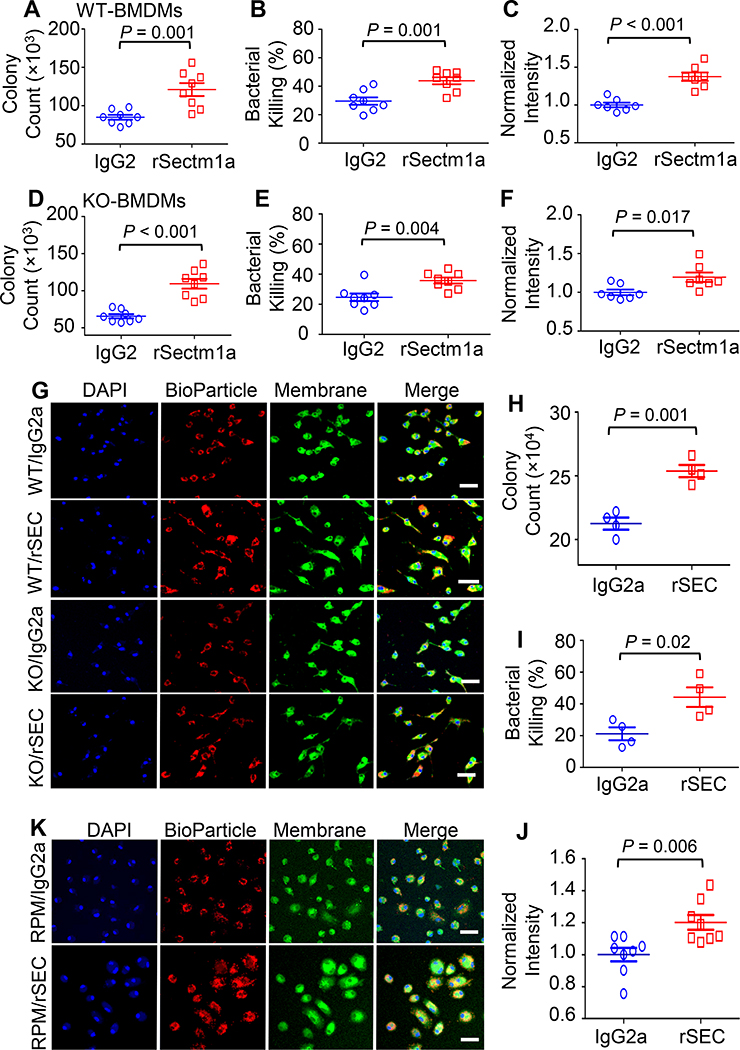
Figure 4. rSectm1a enhances phagocytosis and bactericidal capacity of macrophages.
Effects of rSectm1a (rSEC) on the phagocytic activity and bacterial killing were determined in BMDMs isolated from WT/KO mice and RPMs obtained from WT mice. All macrophages were pre-treated with rSectm1a (rSEC, 800 ng/ml) or IgG2a (500 ng/ml, stoichiometrically matched amount) for 20 h before incubating with mouse serum-opsonized E. coli or red fluorescence-conjugated pHrodo™ E. coli bioparticles. (A-C) rSectm1a treatment significantly increased the capacity of WT-BMDMs to phagocytize (A) and kill live E. coli (B). (C) Red fluorescence-conjugated pHrodo™ E. coli bioparticles were used to confirm phagocytosis assay results. n =7–8. (D-F) The same design strategy was applied to BMDMs isolated from Sectm1a-KO mice. Pre-treatment with rSectm1a restored phagocytic (D) and killing (E) capacity of KO-BMDMs in response to live E. coli challenge. (F) The rSectm1a-induced increase in phagocytic capacity was confirmed using red fluorescence-conjugated pHrodo™ E. coli bioparticles. n =7–8. (G) Representative confocal images of phagocytosis assay in WT-BMDMs and KO-BMDMs with red fluorescence-conjugated pHrodo™ E. coli bioparticles. Scale bar, 20 μm. (H-J) rSectm1a significantly up-regulated the capacity of WT-RPMs to phagocytize (H) and kill live E. coli (I) (n = 4). (J) Red fluorescence-conjugated pHrodo™ E. coli bioparticles were used to confirm phagocytosis assay result with live bacterial (n = 8). (K) Representative confocal images of phagocytosis assay in WT-RPM with red fluorescence-conjugated pHrodo™ E. coli bioparticles. Scale bar, 20 μm. Data are representative of two (H-I) or three (A-F, J) independent experiments. All results are presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by student’s t test.