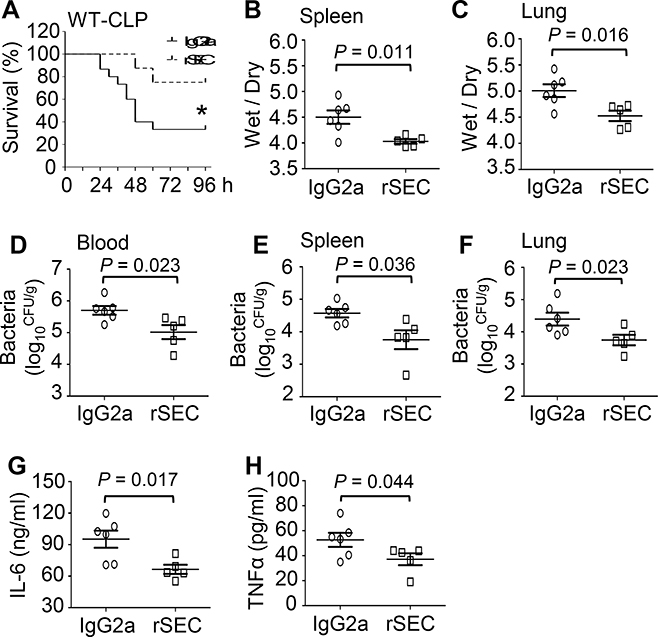
Figure 5. Administration of rSectm1a in CLP-mice decreases mortality, bacterial load, organ damage and systemic inflammation.
WT mice were subjected to a single i.v. dose of rSectm1a (rSEC: 300 μg/kg) or IgG2a (190 μg/kg, stoichiometrically matched amount) at 0.5 h post-CLP surgery. (A) Survival was monitored for 4 days (*, P < 0.05; n = 8 for rSectm1a-treated group, n=15 for IgG2a-treated group). (B and C) The spleen and lung tissues were collected from both IgG2a-treated and rSectm1a-treated mice at 24 h post-CLP, and wet weight to dry weight ratios of spleen (B) and lung (C) were quantified (n = 5–6). (D-F) Bacterial burdens in blood (D), spleen (E) and lung (F) were compared between two treatment groups at 24 h post-CLP (n = 5–6). (G-H) Serum levels of cytokines (G: IL-6 and H: TNFα) of two mouse groups were measured at 24 h after CLP surgery (n = 5–6). Data are representative of two independent experiments. The survival results were analyzed by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. All other results are presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by student’s t test.