Extended Data Fig. 1. Lysine 263 (K263) within the cytoplasmic domain of PD-L1 is acetylated.
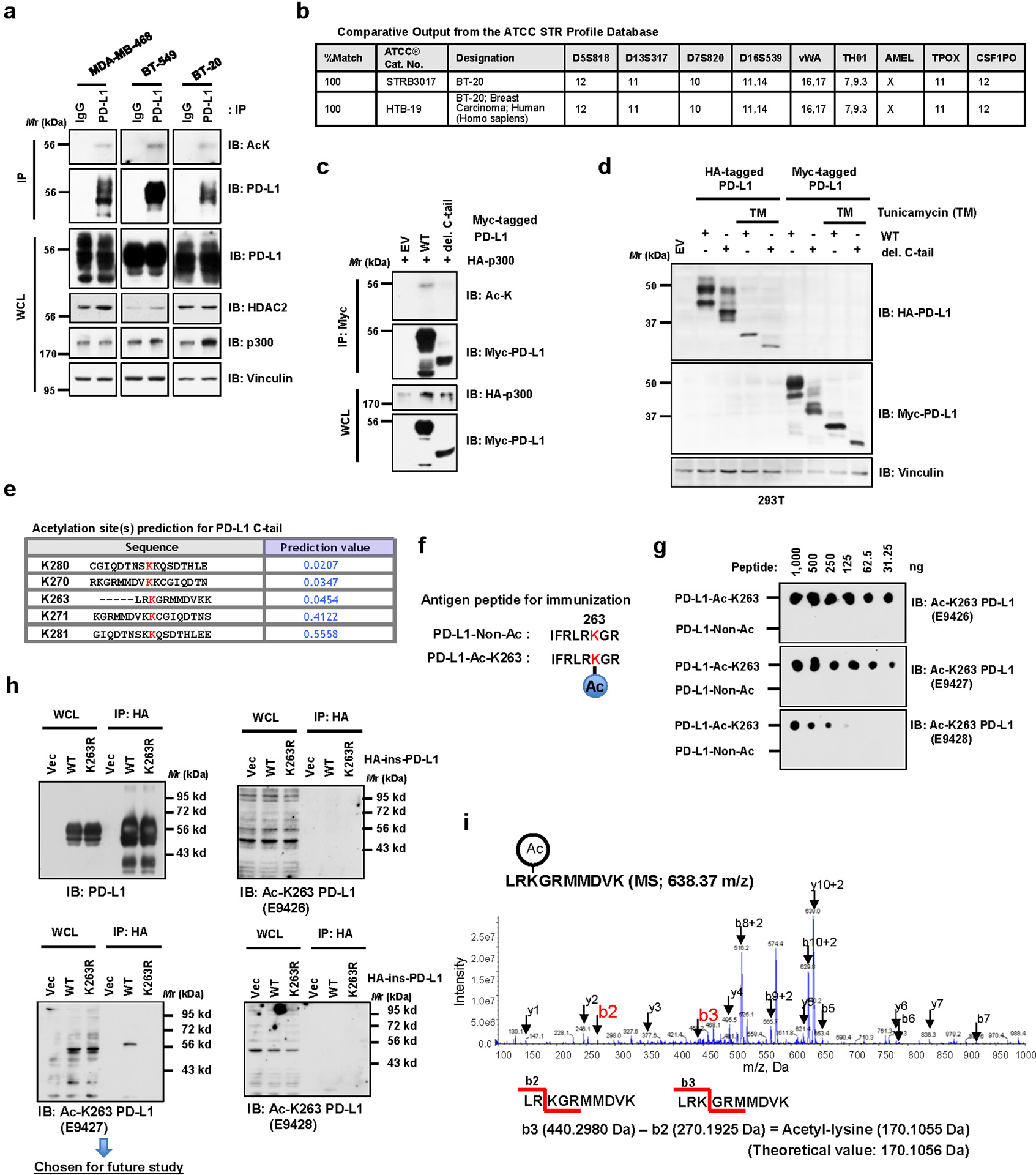
a, Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole-cell lysates (WCL) and anti-PD-L1 immunoprecipitates (IPs) derived from MDA-MB-468, BT-549 and BT-20 cells. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) served as a negative control. b, Authentication results of the BT-20 cell line performed by ATCC. c, IB analysis of WCL and anti-Myc IPs derived from 293T cells transfected with HA-p300 and Myc-full length (FL) PD-L1 or the deletion mutant of C-tail (amino acids (AA) 263–290). d, IB analysis of WCL derived from 293T cells transfected with HA-tag-inserted (HA-ins) or Myc-tagged wild-type (WT) or del. C-tail PD-L1 with or without 1 μg/ml tunicamycin treatment overnight. e, Predicted lysine acetylation sites by the Web Server for KAT-specific Acetylation Site Prediction (ASEB) analysis. f, A schematic diagram of the PD-L1 Lys263 acetylated peptide and non-acetylated peptide used for immunization to generate the anti-Ac-K263 PD-L1 antibody. g, Dot-blot testing of acetylated and non-acetylated peptides using indicated purified antibodies. h, IB analysis of WCL and anti-HA IPs derived from 293T cells transfected with HA-ins-PD-L1 WT or the K263R mutant. i, Mass-spectrometry detection of Lys263 acetylation using a synthetic peptide (AA 261 to 270) following in vitro acetylation assay. The blots and western blots in a, c, d, g and h were performed for n=2 independent experiments with similar results. Unprocessed immunoblots are shown in Source Data Extended Data Fig. 1.
