Figure 4. Second-generation cam16-wt15–33 TriKE displays stronger activity after short-term exposure.
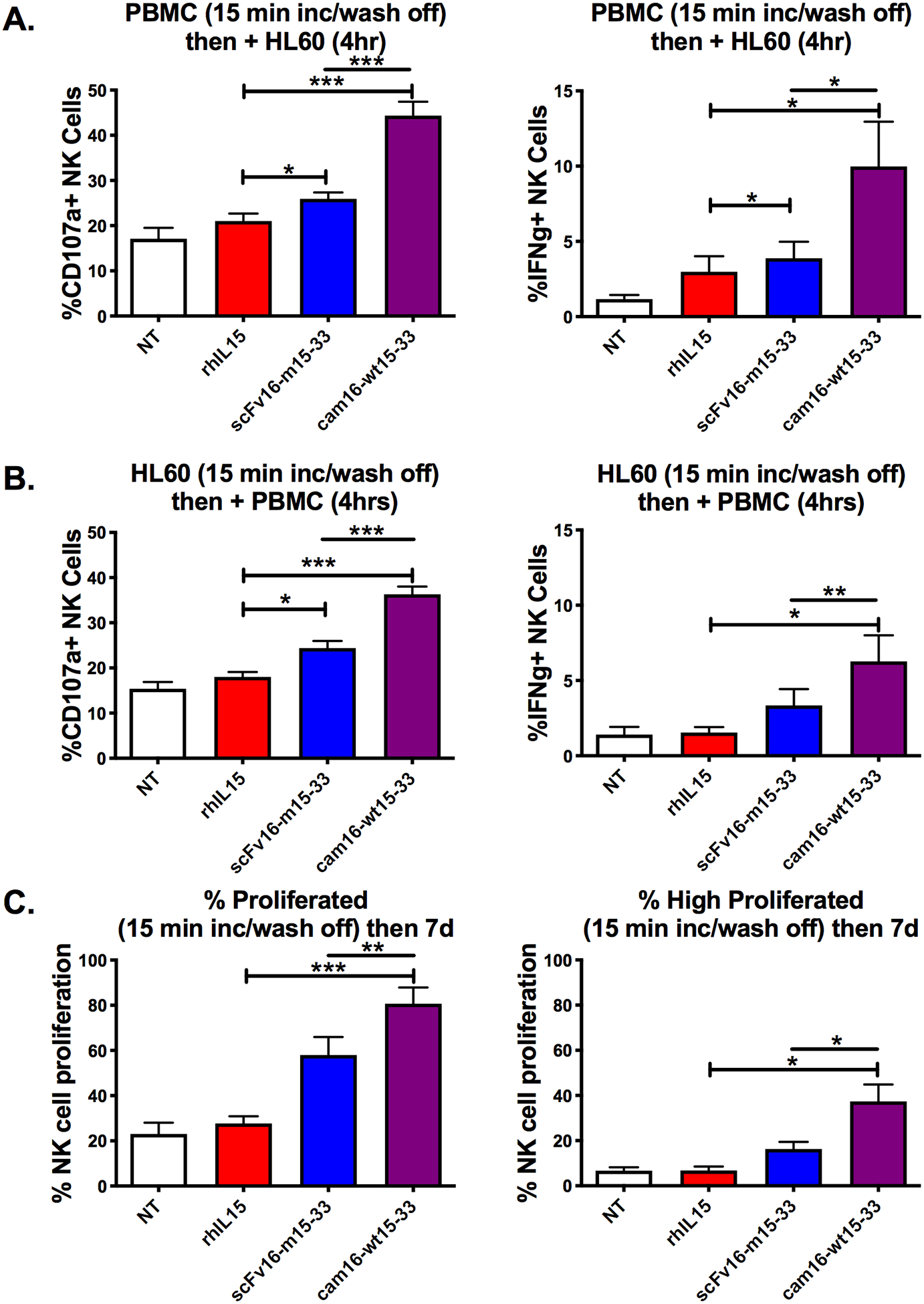
(a) PBMCs were incubated with the indicated treatments (30 nM) for 15 minutes, washed twice, and then incubated with HL-60 targets for 4 hours prior to evaluation of NK cell degranulation and IFNγ production (N=8). (b) HL-60 targets were incubated with the indicated treatments (30 nM) for 15 minutes, washed twice, and then incubated with PBMCs for 4 hours prior to evaluation of NK cell function (N=8). (c) PBMCs were CellTrace labeled, incubated with indicated treatments for 15 minutes, washed twice, and incubated for 7 days in culture with media (no cytokines) to evaluate total NK cell proliferation or those that highly proliferated (N=4). One-way ANOVA with repeated measures was used to calculate differences against the rhIL15 control (brackets), and TriKEs were compared with paired T test (lines). Bars show mean ± SEM and statistical significance as *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 (NT: no treatment control).
