Figure 6. Ets1 activity depends on MAPK signaling and phosphorylation of conserved Thr30 and Ser33 residues.
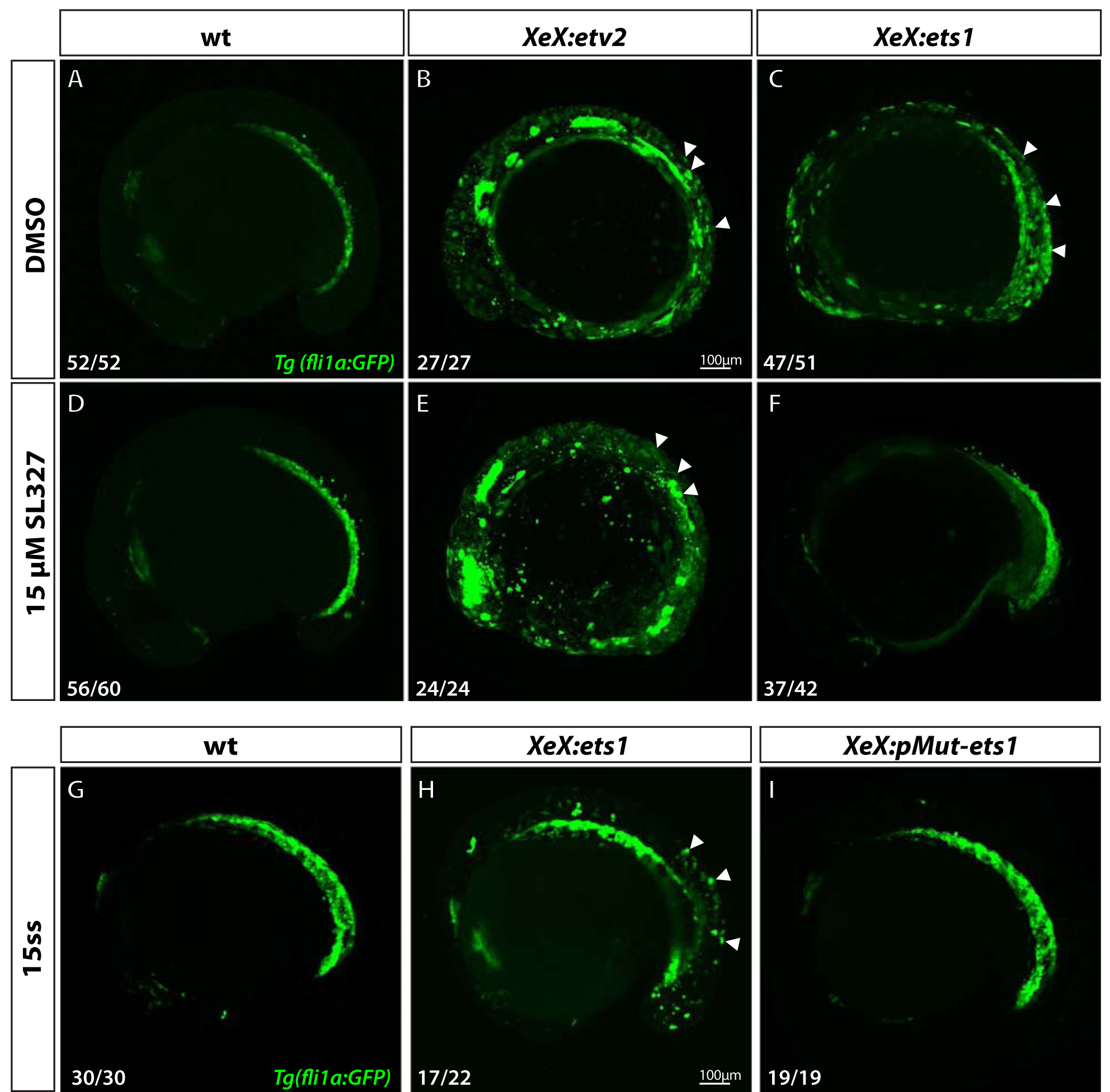
(A-F) Confocal micrographs of 12-somite stage Tg(fli1a:GFP) wild-type, XeX:etv2 and XeX:ets1- injected embryos treated with either DMSO (A-C) or 15 μM MAPK inhibitor SL327 (D-F) from 70% epiboly-12-somite stage. Note the absence of ectopic GFP fluorescence in XeX:ets1 embryos treated with SL327 (F) compared to those treated with DMSO (C). (G-I) Confocal micrographs of 15-somite stage Tg(fli1a:GFP) wild-type embryos, XeX:ets1 and XeX:pMut-ets1 (containing Thr30Ala and Ser33Ala mutations) embryos. Note the reduction of ectopic GFP expression in embryos injected with the XeX:pMut-ets1 construct containing mutated phosphorylation sites (I) compared to XeX:ets1-injected embryos (H). White arrowheads indicate ectopic GFP expression.
