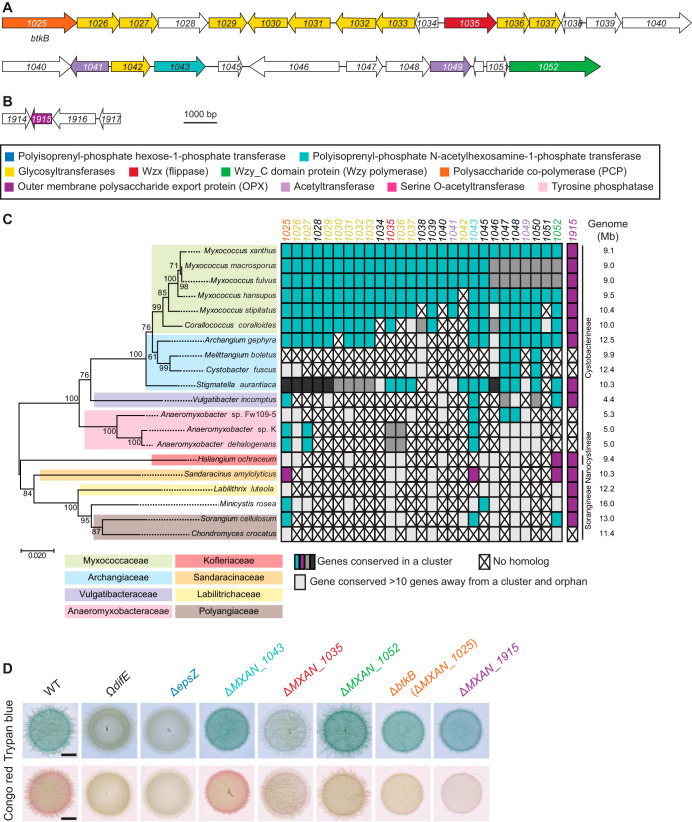
FIG 3.
Bioinformatics and genetic analysis of the MXAN_1025-1052/_1915 loci. (A and B) MXAN_1025-1052 and _1915 loci in M. xanthus. Genes are drawn to scale, and the MXAN number or gene name is indicated (Table S2). The color code indicates predicted functions as indicated in the key and is used throughout. (C) Taxonomic distribution and synteny of genes in the MXAN_1025-1052/_1915 loci in Myxococcales with fully sequenced genomes. A reciprocal best BLASTP hit method was used to identify orthologs. (Left) 16S rRNA tree of Myxococcales with fully sequenced genomes. (Right) Genome size, family, and suborder classification are indicated. To evaluate gene proximity and cluster conservation, 10 genes was considered the maximum distance for a gene to be in a cluster. Genes found in the same cluster (within a distance of <10 genes) are marked with the same color (i.e., cyan, magenta, and dark and medium gray). Light gray indicates a conserved gene that is found somewhere else on the genome (>10 genes away from a cluster); a cross indicates no homolog found. (C) Determination of EPS synthesis. Twenty-microliter aliquots of cell suspensions of strains of the indicated genotypes at 7 × 109 cells ml−1 were spotted on 0.5% agar supplemented with 0.5% CTT and Congo red or trypan blue and incubated 24 h. The ΩdifE mutant served as a negative control. Scale bars, 3 μm.