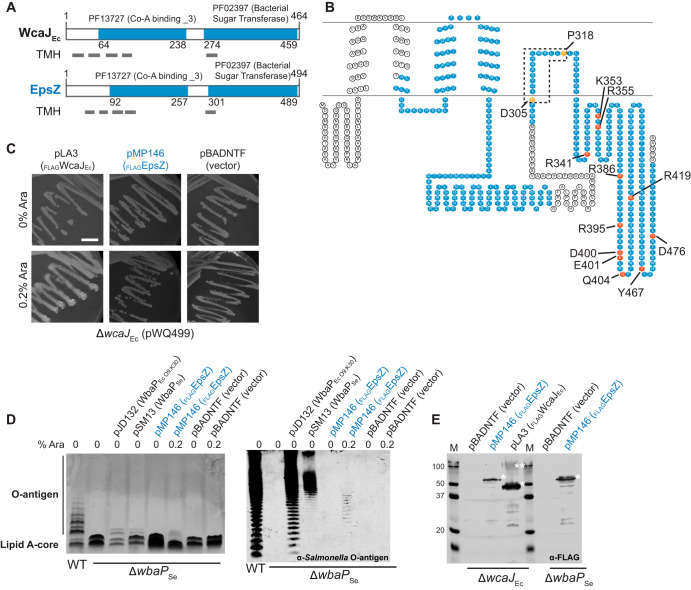
FIG 5.
Polyisoprenyl-phosphate hexose-1-phosphate (PHPT) activity of MXAN_7415. (A) Domain and TMH prediction of EpsZ (MXAN_7415) and WcaJ of E. coli (WcaJEc). Gray rectangles indicate TMH. Numbers indicate domain borders. (B) Topology predictions for EpsZ (MXAN_7415). Domains are indicated in blue, and conserved amino acids important for structure or activity of the protein are marked with orange and red, respectively. Sequence alignment of EpsZ (MXAN_7415) with WbaPSe is shown in Fig. S1. (C to E) Complementation of colanic acid synthesis and LPS O antigen in E. coli K-12 W3110 (ΔwcaJEc) and S. enterica LT2 (ΔwbaPSe) mutants, respectively, by plasmids encoding the indicated PHPT proteins. (C) The E. coli ΔwcaJEc mutant XBF1 containing pWQ499 (RcsA+) and the indicated complementing plasmids or vector control on LB plates was incubated overnight at 37°C with 10 μg ml−1 tetracycline (to maintain pWQ499) and with or without arabinose (Ara) to induce gene expression. Incubation was extended to 24 to 48 h at room temperature to further increase colanic polysaccharide synthesis. Scale bar, 1 cm. (D) Complementation of S. enterica Typhimurium LT2 ΔwbaPSe mutant containing the indicated plasmids. LPS samples were extracted, separated by electrophoresis on SDS–14% polyacrylamide gels, and silver stained (left) or examined by immunoblotting using rabbit Salmonella O antiserum group B (right). Each lane corresponds to LPS extracted from 108 cells. Cultures included addition of arabinose as indicated. (E) Immunoblot using anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody to confirm expression of FLAGMXAN_7415 and FLAGWcaJ in the ΔwcaJ mutant and the expression of FLAGMXAN_7415 in S. enterica. Note that WbaP expressed from pSM13 was not tested, since it is not fused to a FLAG tag. Single and double asterisks denote the monomeric and oligomeric forms of the PHPT proteins, respectively, usually present under the gel conditions required to ensure their visualization.