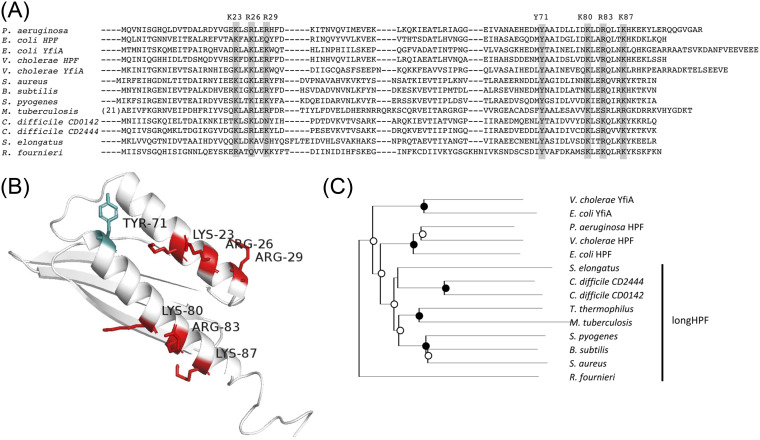
FIG 2.
(A) Sequence alignment of the HPF and YfiA from distantly related species of bacteria. The entire HPF or YfiA sequence is shown for the gammaproteobacteria, whereas only the N-terminal domain is shown for the long-HPF of Gram-positive bacteria and mycobacteria. The rectangles show the conserved positively charged amino acids and conserved tyrosine 71 residue that reside within the HPF two alpha helices. The highlighted amino acids of the P. aeruginosa HPF were targets for site-directed mutagenesis studies here. (B) Model of HPF from P. aeruginosa obtained using I-Tasser, highlighting the amino acids targeted for site-directed mutagenesis. (C) Phylogenetic tree of HPF from distantly related bacteria. Black circles indicate bootstrap values of 100%, and open circles indicate bootstrap values of greater than 50%.