Figure 1. General Schematic for Parallel Chemoselective Profiling.
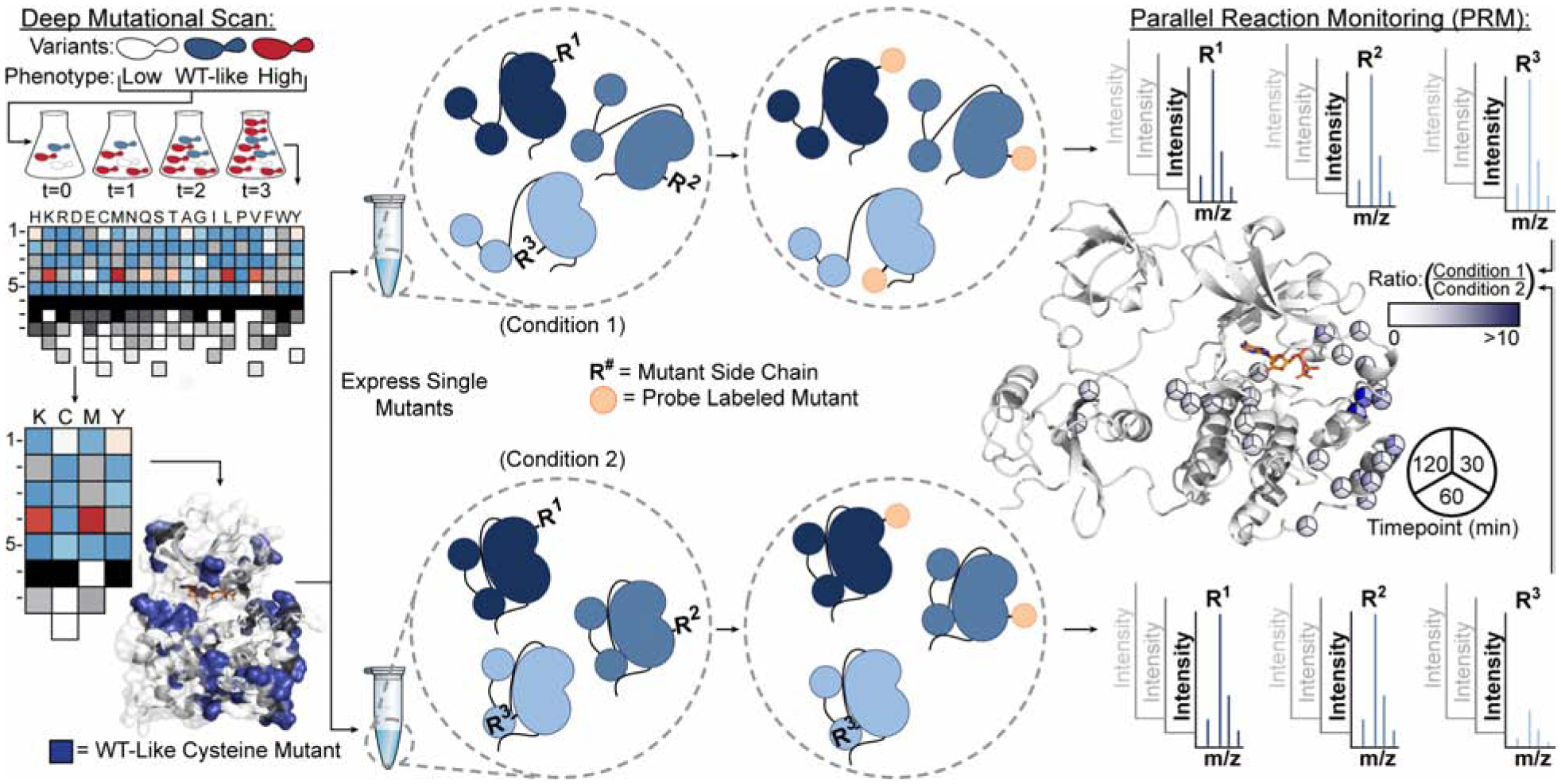
Deep Mutational Scanning is used to determine positions where chemically reactive reporter amino acids can be installed on a protein of interest without perturbing protein function. Individual mutants are expressed and purified in a pooled format and are treated under comparative conditions in vitro. Following treatment, solvent exposed mutant residues are labeled with a chemoselective reagent. Unreacted mutant residues are then capped under denaturing conditions, protein is digested, and labeled residues are quantified using Parallel Reaction Monitoring targeted mass spectrometry. Ratios of labeled residues are compared across timepoints or labeling reagent conditions, which can be visualized and used to infer changes to the local environment of each mutant residue.
