Figure 1.
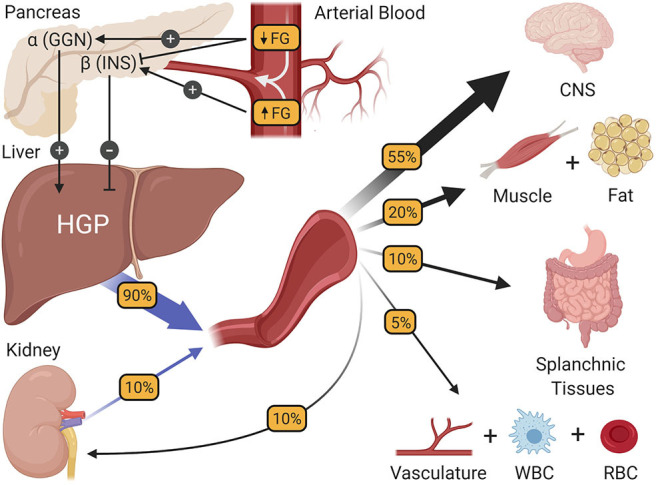
The regulation of fasting blood glucose homeostasis. Subtle changes in fasting glucose levels (FG) entering the pancreas regulate the release of the islet hormones insulin (INS) and glucagon (GGN). In turn, these hormones control the rate of hepatic glucose production (HGP), making HGP equal to the rate at which all other tissues of the body utilize glucose, thereby preserving fasting glucose levels at a steady state. CNS, central nervous system; WBC, white blood cells; RBC, red blood cells.
