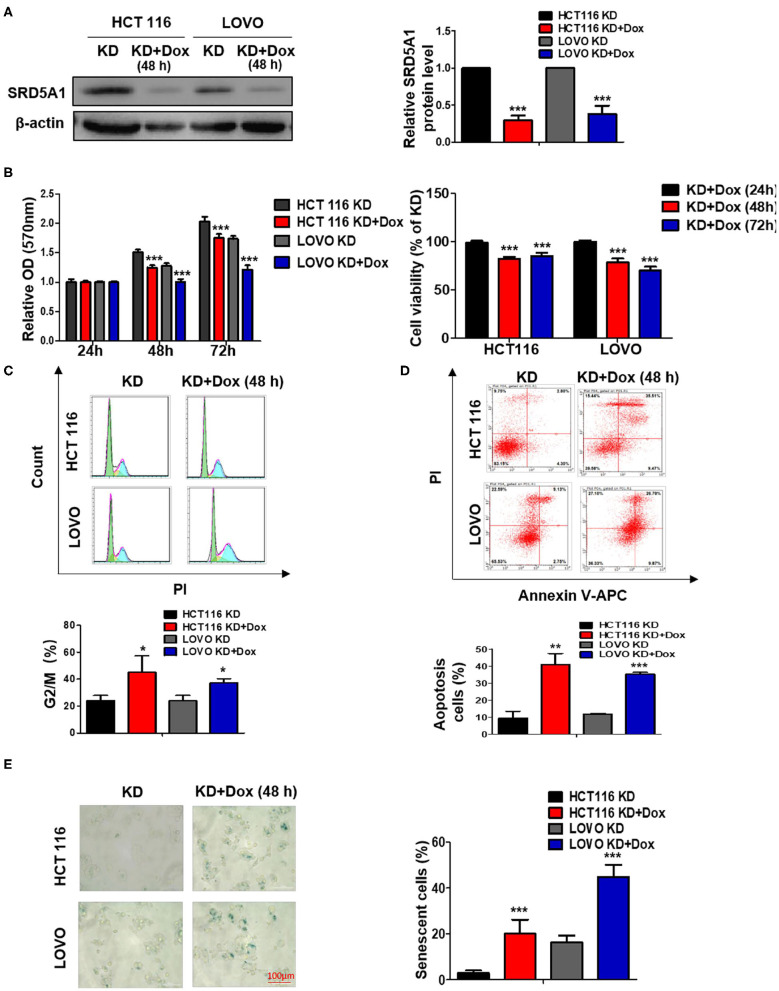
Figure 2.
Genetic knockdown (KD) of SRD5A1 mitigates cell proliferation, enhances cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and senescence in CRC cells. (A) Western blot results validated the decreased protein levels of SRD5A1 after SRD5A1-shRNA transfection in HCT116 and LOVO cells. Transfected cells were screened using puromycin and induced with doxycycline (2 μg/ml) for 48 h (KD + Dox). Control group without induction (KD). (B) Evaluation of cell viability was analyzed by MTT proliferation assay after SRD5A1-shRNA transfection for 24, 48, and 72 h. Inhibition of SRD5A1 expression led to reduced cell viability of HCT116 and LOVO in a time-dependent manner significantly. (C) Distribution of SRD5A1KD and SRD5A1KD+DOX cells in different phases of the cell cycle was determined by flow cytometry after treated for 48 h. Inducible downregulation of SRD5A1 triggered HCT116 and LOVO cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase. (D) Flow cytometry illustrated that attenuated expression of SRD5A1 resulted in a higher level of apoptosis using Annexin-V-FITC apoptotic assay after a 48-h treatment. (E) SA-β-galactosidase (Green) cellular senescence staining showed that cellular senescence was accelerated by suppression of SRD5A1. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. Experiments were repeated three times.