Fig. 4.
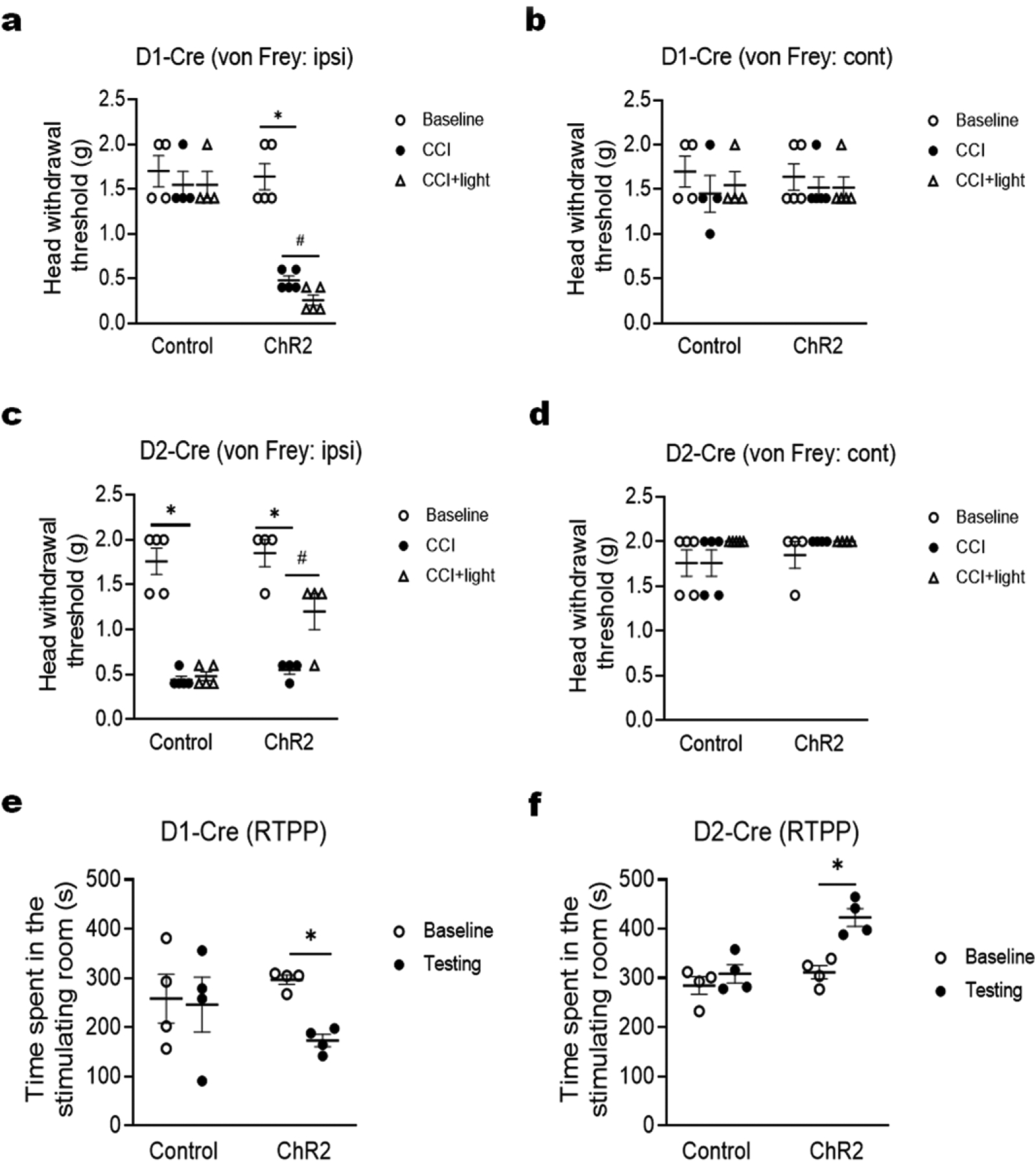
Optogenetic activation of ACC dopamine receptor D1-expressing neurons and D2-expressing neurons oppositely modulates trigeminal neuropathic pain on day 14 after CCI-ION. (a and c) In D1-Cre mice (a), optogenetic activation of ACC D1 neurons further decreased head withdrawal threshold in the ipsilateral side; in D2-Cre mice (c), optogenetic activation of ACC D2 neurons reversely increased head withdrawal threshold in the ipsilateral side. (b and d) In both D1-Cre (b) and D2-Cre (d) mice, the CCI-ION and optogenetic stimulation had no effect on head withdrawal threshold in the contralateral side. (e and f) In the real-time place preference (RTPP) test, optogenetic activation of ACC D1 neurons (e) significantly decreased the time spent in stimulating room, but optogenetic activation of ACC D1 neurons (f) significantly increased the time spent in stimulating room. n = 6 per group. *P < 0.05 vs. the corresponding Baseline values; #P < 0.05 vs. the corresponding CCI group.
