Fig. 1:
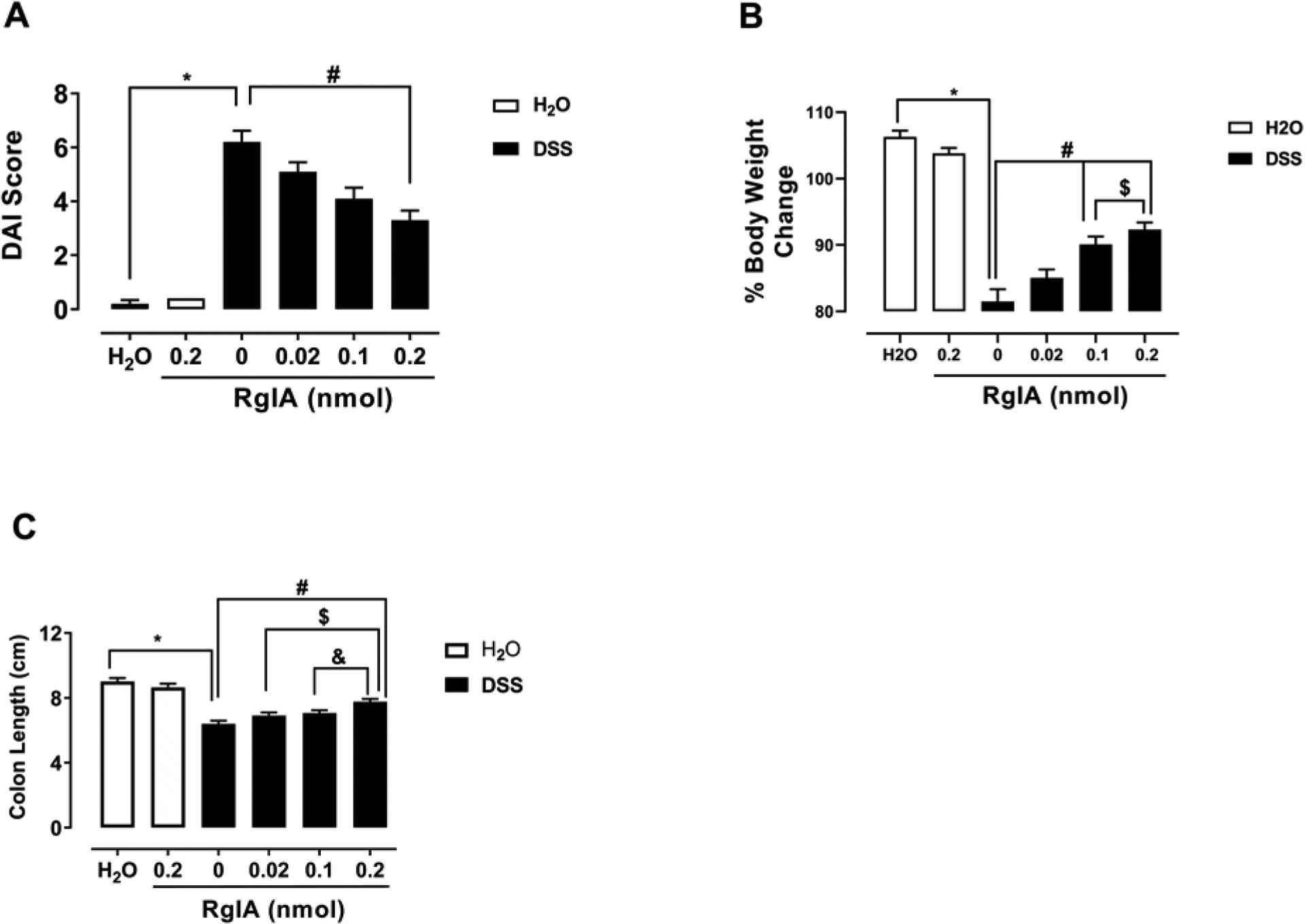
α-RgIA treatment reverses clinical signs of colitis in a mouse model. A) The repeated administration of α-RgIA only at dose of 0.2 nmol/mouse, s.c. reverses the increased DAI induced by DSS; * P<0.0001 DSS-Saline vs. Water-Saline; # P<0.01 DSS-Saline vs. α-RgIA at dose of 0.2 nmol/mouse. B) The repeated administration of α-RgIA at doses of 0.1 and 0.2 nmol/mouse, s.c. attenuate the decreased percentage of body weight change induced by DSS; * P<0.0001 DSS-Saline vs. Water-Saline; # P<0.0001 DSS-Saline vs. α-RgIA at dose of 0.1 and 0.2 nmol/mouse; $ P<0.01 α-RgIA 0.1 vs. 0.2 nmol/mouse. C) The repeated administration of α-RgIA only at dose of 0.2 nmol/mouse, s.c. rescued the shortening of the colon length; * P<0.0001 DSS-Saline vs. Water-Saline; # P<0.0001 DSS-Saline vs. α-RgIA at a dose of 0.2 nmol/mouse; $ P<0.01 α-RgIA 0.02 vs. 0.2 nmol/mouse; & P<0.05 α-RgIA 0.1 vs. 0.2 nmol/mouse; DAI, Disease Activity Index; DSS, dextran sodium sulfate n= 11 mice/group; data expressed as mean ± SEM.
