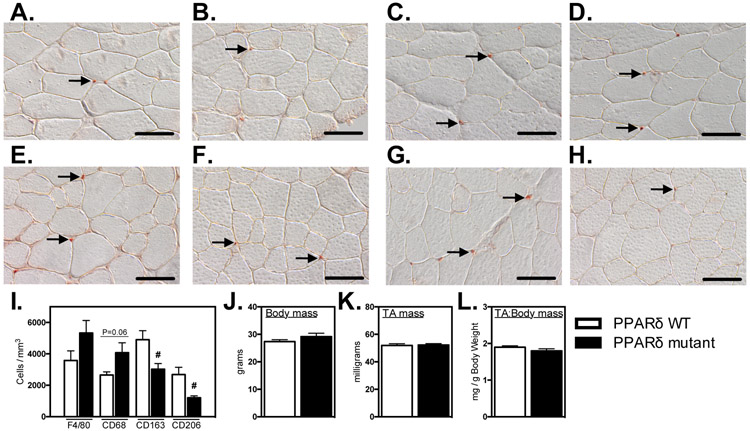
Figure 3.
Ablation of Ppard in myeloid cells reduces M2-biased macrophages in healthy muscle without affecting muscle mass. A-H: Cross-sections of non-injured Ppard WT (A, C, E, G) and mutant (B, D, F, H) TA muscles were immunolabeled with anti-F4/80 (A, B), anti-CD68 (C, D), anti-CD163 (E, F) or anti-CD206 (G, H). Representative, positively labeled cells are indicated with arrows. Scale bars = 50 μm. I: Quantification of numbers of immunolabeled cells per sectioned muscle volume show that CD163+ and CD206+ cells were reduced in muscles of mutants. J-L: Myeloid Ppard deficiency did not affect body mass (J), TA muscle mass (K) or TA muscle mass-to-body mass ratio (L). # indicates significant difference (P < 0.05) from Ppard WT. P-values based on two-tailed t-test. N = 4-5 for each data set. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.