Figure 1:
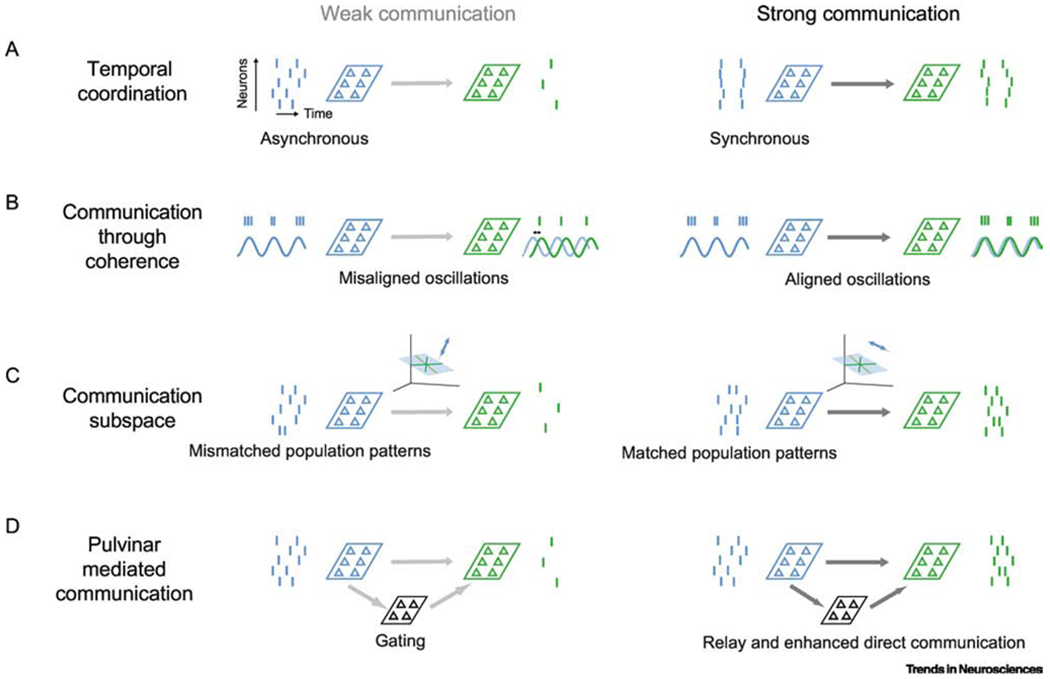
Schemes for modulating corticocortical communication. (A) Temporal coordination. Left: Weak communication occurs when source population activity (blue) is asynchronous, resulting in little activity in the target network (green). Strong communication (right) occurs when source activity is synchronous. In the schematic on the right, resultant downstream activity is depicted as synchronous as well, as in [26], though it remains unclear whether in the cortex downstream activity driven by input synchrony is also synchronous or simply elevated. (B) Communication through coherence. Left: Weak communication occurs when oscillations in the source and target area are not appropriately phase aligned. Activity in the source area occurs at the peak of a local oscillation. If the phase of this oscillation is misaligned with the oscillation in the target network, there is little activity generated in the target (faint blue line, source oscillation; green line, oscillation in the target network). Right: Strong communication occurs when the two oscillations have appropriate phase offset. (C) Communication subspace. Left: Weak communication occurs when activity in the source population is mismatched to the communication subspace that relates source activity to target activity. In this illustration, the subspace is indicated as a plane in the source population activity space; fluctuations in the source area are orthogonal to the subspace and thus generate no activity in the target network. Right: Strong communication occurs when fluctuations in source activity fall in the communication subspace. (D) Pulvinar mediated communication. Left: Weak communication through both the direct corticocortical pathway and indirect pathway through the pulvinar. Weak communication may involve gating mechanisms in the thalamus. Right: Strong communication involves better relaying of activity through the pulvinar, and enhanced direct corticocortical communication. Text alignment under the source/targets areas in each panel indicate whether the schemes involves changes in the source network, target network, or in between.
