Fig. 1:
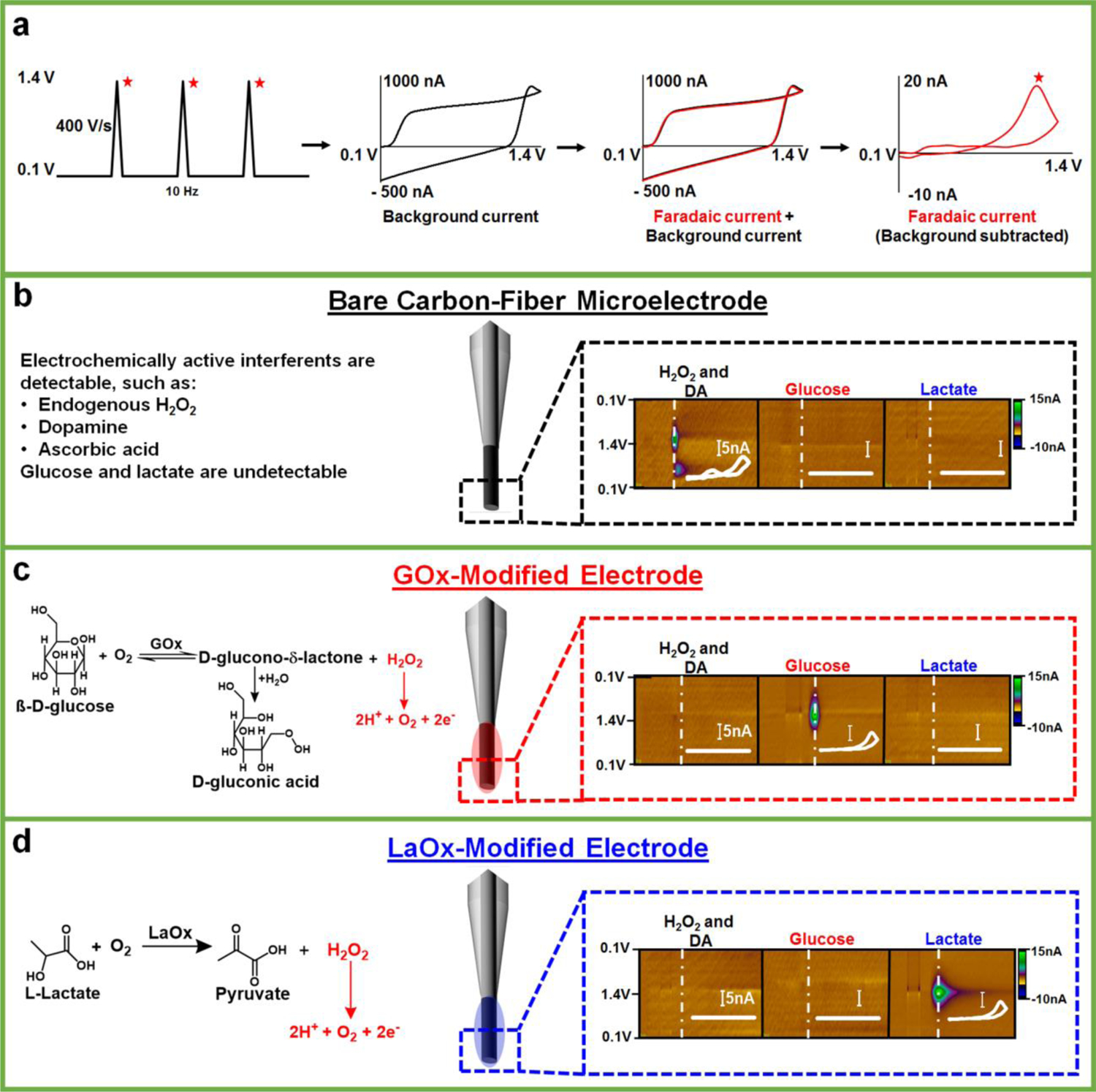
Carbon-fiber microbiosensors coupled with FSCV. (a) The triangular waveform, ranging from +0.1 V to 1.4 V, is applied at 10 Hz. This generates a large background current (black), which is subtracted to reveal faradaic current (right, red) specific to a given analyte, for example H2O2. (b-d) Voltammetric detection of H2O2, DA, glucose, and lactate at bare and enzyme-modified carbon-fiber microelectrodes, with appropriate enzymatic reactions (if applicable). Representative color plots are shown with inset background subtracted cyclic voltammograms (scale bar is 5 nA). H2O2 (50 μM) and DA (1 μM) can be simultaneously detected on bare microelectrodes with this waveform, but glucose (2.6 mM) and lactate (1 mM) are not inherently electroactive and, therefore, are undetectable. By contrast, glucose and lactate can be detected at microelectrodes modified with the (appropriate) oxidase enzyme, but standards of H2O2 (50 μM) and DA (1 μM) produce little signal [(35–38)].
