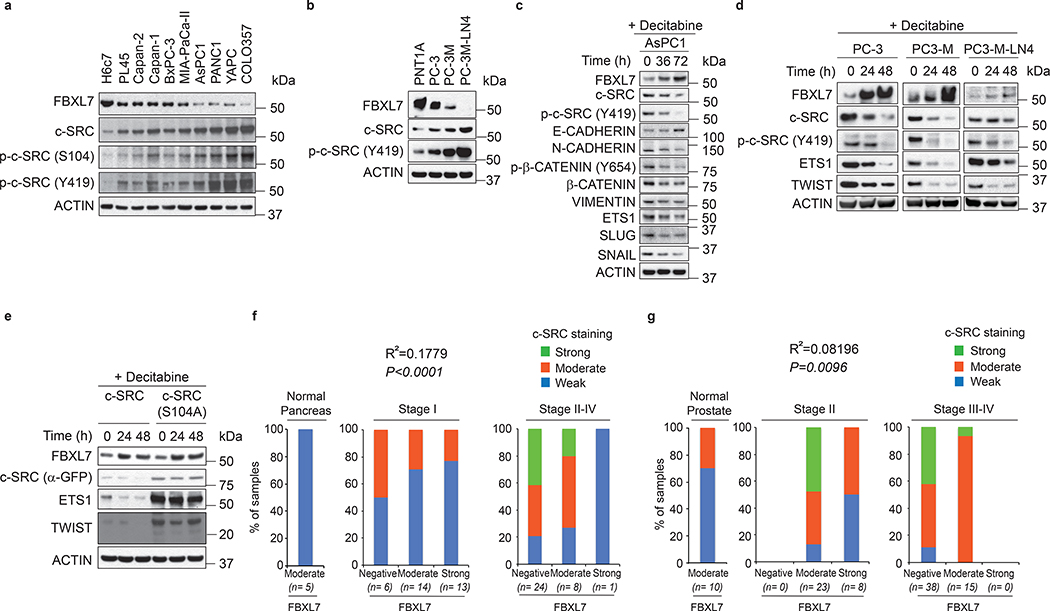
Fig. 5. Downregulation of FBXL7 expression inversely correlates with c-SRC upregulation in pancreatic and high-stage prostate cancers.
a, Protein extracts from normal diploid pancreatic duct epithelial cells (H6c7) and the indicated pancreatic cancer cells were analyzed by immunoblotting.
b, The indicated cells were subjected to immunoblotting.
c-d The indicated cells were treated with decitabine for the indicated times and analyzed by immunoblotting.
e, PC-3 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type c-SRC or c-SRC(S104A). Twenty-four hours after, cells were treated with decitabine for the indicated times and immunoblotted.
a-e, Two independent experiments were performed with similar results.
f, Tumor microarrays (TMAs) containing normal and tumor pancreatic human specimens were immunostained with antibodies to FBXL7 and c-SRC. The graphs show the percentage of normal, Stage I and Stage II-IV tumor pancreatic tissues with no, moderate or strong FBXL7 expression that have no, moderate or strong c-SRC expression. n = 71 biologically independent samples. Linear regression was determined using X2 test.
g, TMAs containing normal and tumor human prostate specimens were immunostained with antibodies to FBXL7 and c-SRC. The graphs show the percentage of normal, Stage II, and Stage III/IV prostate cancer tissues with no, moderate, or strong FBXL7 expression that have no, moderate, or strong c-SRC expression. n = 94 biologically independent samples. Linear regression was determined using Γ2 test.