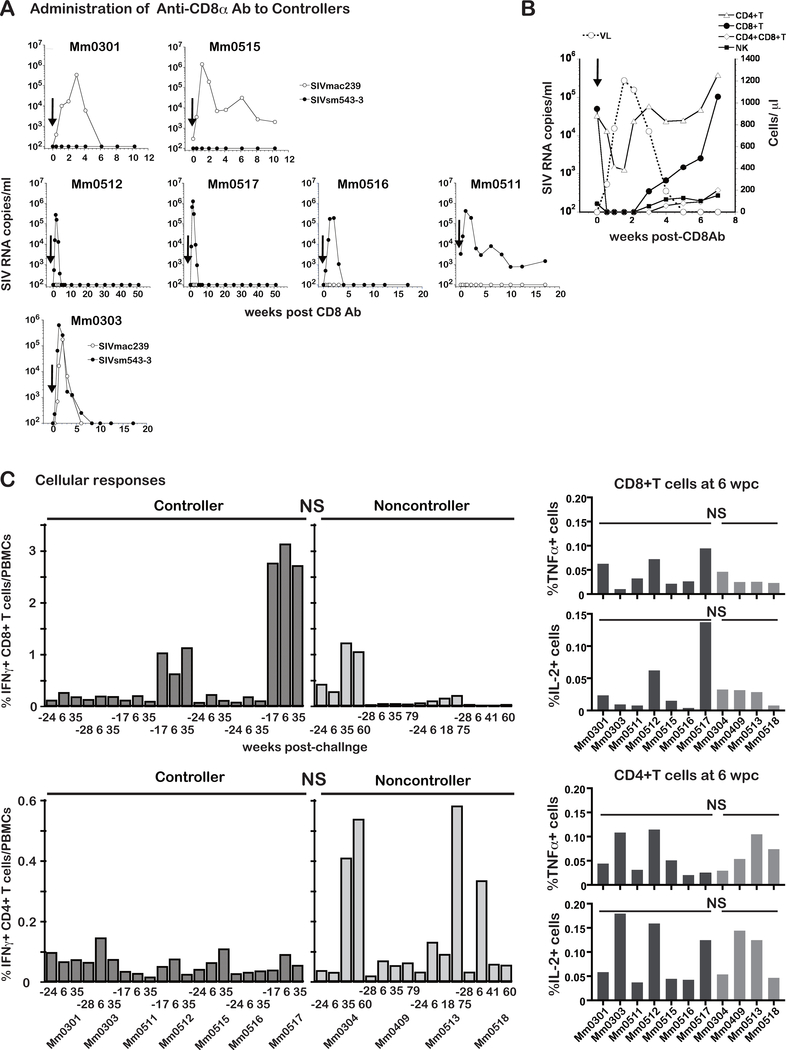
Fig. 1. CD8+ cells mediated immune responses are required for containment of SIV infection.
A: Plasma viral loads of seven controller animals following the in vivo administration of an anti-CD8α antibody (CD8 Ab) administration (shown by arrows). Two of the animals (Mm0301 and Mm0515) had viremia due to the vaccine but not challenge virus. Four animals (Mm0512, Mm0517, Mm0516 and Mm0511) had viremia of the heterologous challenge but not vaccine virus. Mm0303, however, had viremia due to both challenge and vaccine virus origin.
B: Correlation of the absolute number of CD4+ T, CD8+ T, CD4+CD8+ T and NK cells with plasma viral load kinetics in a representative animal (Mm0512) following the in vivo administration of CD8 Ab.
C: SIV specific cellular responses. PBMCs from the controller (n = 7) and non-controller animals (n = 4) were incubated with a pool of overlapping SIV peptides encompassing the viral proteins (Gag, Pol, Env, Vif, Vpr, Vpx, Tat, Rev, and Nef) of SIVmac239 and the frequencies of IFNγ expressing cells are shown. The PBMC samples analyzed were collected pre-challenge (−28, −24 or −17 weeks prior to the challenge), and at 6, 35, 41, 60, and 75 weeks post-challenge with SIVsmE543–3. Responses of SIV specific CD8+ T cells (left upper panel) and SIV specific CD4+ T cells (left lower panel) are shown for the frequencies of IFNγ expressing cells. Responses of SIV specific CD8+ T cells (right upper panel) and SIV specific CD4+ T cells (right lower panel) at 6 wpc are shown by the frequencies of TNFα and IL-2 expressing cells. Differences in the cellular responses of the controller and non-controller were not significant (NS) (p >0.05) by Mann-Whitney t test.