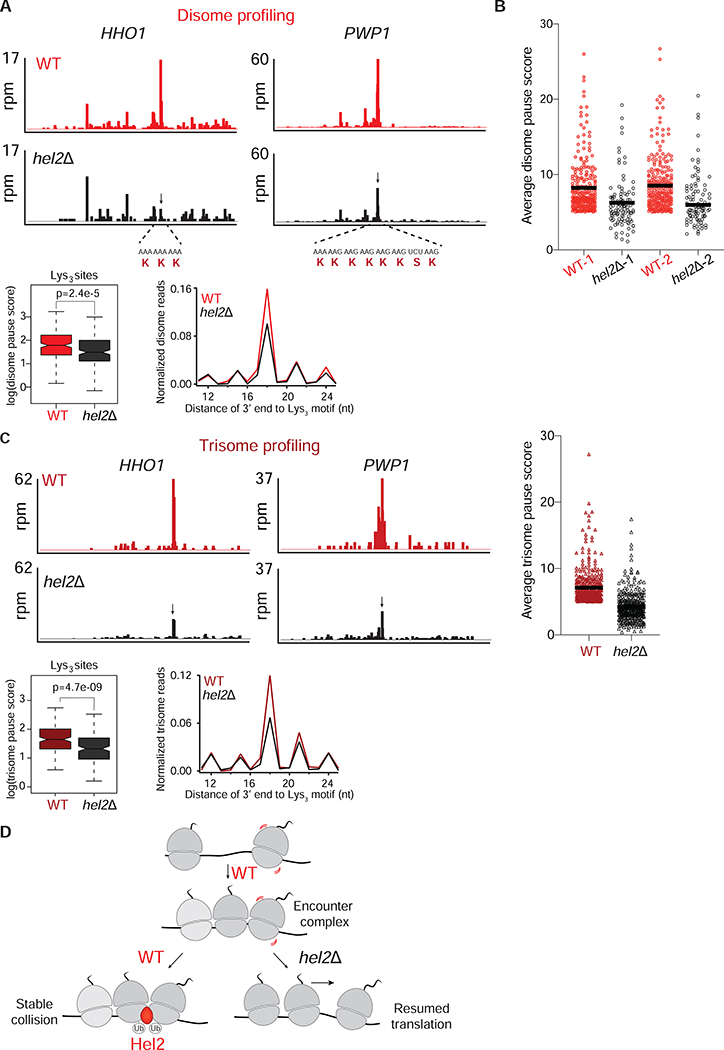
Figure 4: Loss of Hel2 decreases disome and trisome formation at various motifs.
A. Top panels: Disome profiles of HHO1 and PWP1 genes in WT (red) and hel2Δ (black) cells. The disome peak that is sensitive to Hel2 loss is shown by a black arrow. mRNA and amino acid sequences mapping to the disome peaks are shown in red. Bottom: Average, normalized disome reads mapped to Lys3 motifs from WT (red) and hel2Δ (black) cells. The box plot shows the distribution of individual pause scores from Lys3-coding sites (n=202) in the transcriptome.
B. Average disome pause scores of 261 tripeptide motifs plotted for WT (red) and hel2Δ (black). Each point represents a tripeptide motif that was filtered for having a pause score greater than 5 in WT. The black line inside each distribution represents the mean of the corresponding data. The full distribution of all 6267 motifs is shown in Figure S4B.
C. Top left/center panels: Trisome profiles of HHO1 and PWP1 genes in WT (dark red) and hel2Δ (black) cells. Arrow indicates the trisome peak that is sensitive to Hel2 loss (disome formed at this position shown in A). Top right panel: As shown for disome data in B, average trisome pause scores of 391 tripeptide motifs plotted for WT (dark red), hel2Δ (black) show loss of Hel2 reduces pause scores. The unfiltered distribution of all 6267 motifs is shown in Figure S4B. Bottom panel: Average, normalized trisome reads mapped to Lys3 motifs from WT (dark red) and hel2Δ (black) cells. The box plot shows the distribution of individual pause scores from Lys3-coding sites (n=173).
D. Model of Hel2 action on collisions formed on endogenous mRNAs. In WT cells, upon ribosome stalling, disomes and trisomes are transiently formed (encounter complexes). This encounter complex is recognized and possibly stabilized by Hel2. Ubiquitination activity of Hel2 is important for maintaining these disomes. In the absence of Hel2, the disomes/trisomes are no longer stable and presumably continue translation downstream of the stall site.
See also Figure S4.