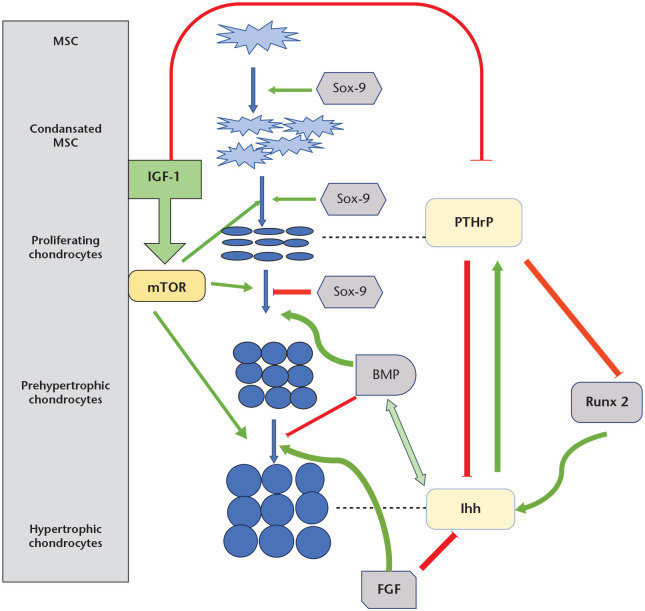
Fig. 2.
Paracrine control of growth plate.
Notes. Ihh (Indian hedgehog) enhances the proliferation and maturation of chondrocytes and induces the expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) in the periarticular region. PTHrP prevents premature hypertrophic differentiation. The negative feedback loop between Ihh and PTHrP keeps chondrocytes in the proliferating state, controls chondrocyte proliferation, and maintains the lengths of columns.
Ihh and bone morphogenic protein (BMP) are in a positive feedback loop with each other and up-regulate chondrocyte proliferation together. In addition, BMP inhibits the development of terminally differentiated chondrocytes.
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signalling is antagonistic to BMP activity. FGF expression down-regulates chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophy by inhibiting Ihh and promotes chondrocyte differentiation.
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) positively regulates Ihh expression and promotes chondrocyte proliferation, but it is inhibited by PTHrP, which is induced by Ihh.
Sox-9 signalling contributes to chondrogenesis in different steps. Sox-9 up-regulates chondrogenic mesenchymal condensation, chondrocyte differentiation, and normal chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits the transition of proliferating chondrocytes to hypertrophy.
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) signalling modulates chondrogenesis by both suppressing PTHrP production and inducing the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling activity, which plays a role in all stages of chondrocyte maturation.