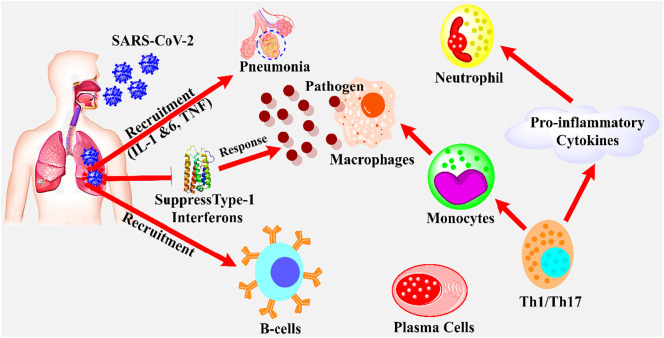
Fig. 3.
The representation of the immune response of host during the infection of SARS-CoV-2. The SARS-CoV-2 binds to the human ACE-2 receptor and inter lung and infected the cells, which arrest the type-1 interferon (INF) to replicate viral RNA genome. The suppression in INF-1 leads to the production of specific first-line defense against pathogens. The B-cells and plasma cells could effectively neutralize the SARS-CoV-2 by producing specific antibodies against virus. The specific cells, namely Th1/Th17 could lead to the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as INF-γ, and monocytes/macrophages which may result in the recruitment of neutrophil production and pathogens ingestion respectively [44].