Fig. 4.
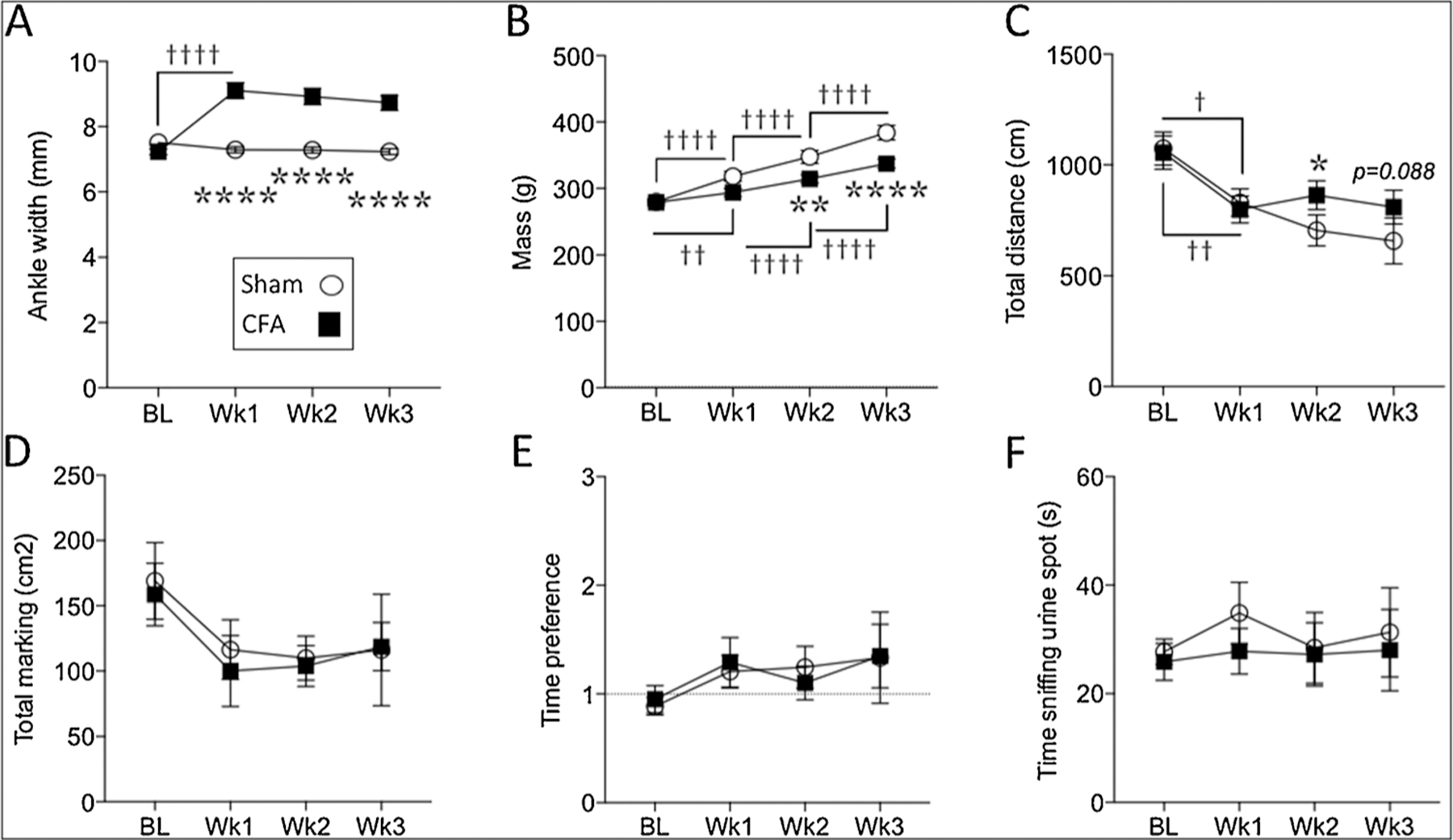
At the group level, CFA-induced persistent inflammation increased ipsilateral ankle width (A), slower weight gain (B) and differences in distance covered (C), but did not alter overall marking area (D), time preference for the female urine zone (E) or sniffing of the female urine spot (F). Two-way mixed design ANOVA. Stars (*) represent a significant comparison between CFA and sham groups. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; **** p < 0.0001. Daggers (†) represent a significant comparison between the time points indicated. † p < 0.05; †† p < 0.01; ††††p < 0.0001.
