Fig. 4.
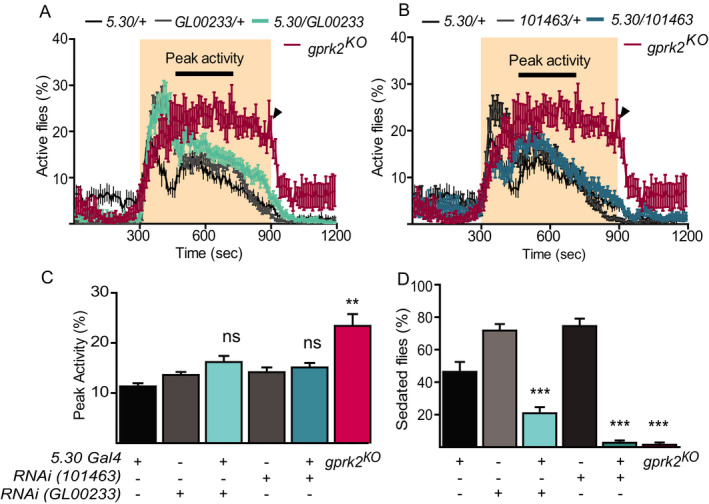
The decreased sensitivity to alcohol is not linked to increased alcohol‐induced hyperactivity when Gprk2 is knocked down in EB neurons. All experimental (cyan in A&B) and control groups were tested at the same time but presented for each RNAi line separately in A and B. Disruption of Gprk2 expression using 2 independent lines (GL00233 and 101463) with EB‐specific driver (5.30) showed no significant difference in 4‐minute peak activity (cyan in C) but decreased sensitivity to alcohol (cyan in D) compared to controls (black and gray in C&D). gprk2KO flies were used as positive controls (magenta, n = 7). n = 11 unless specified. Mean ± SEM. ns, p > 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 according to the 1‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test after the data passed the Kolmogorov‐Smirnov normality test.
