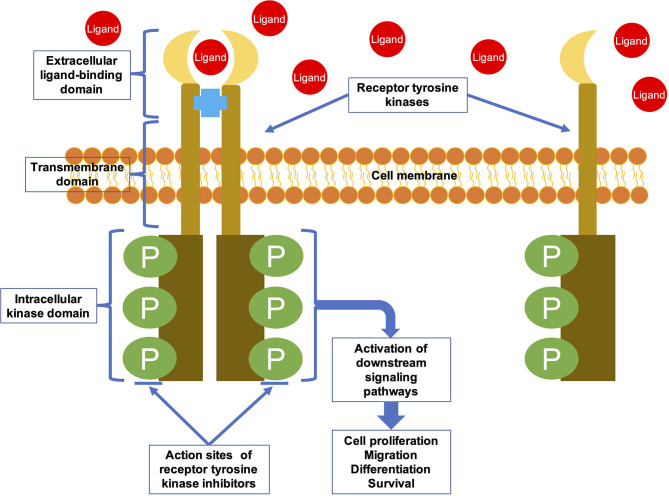
Figure 1.
The general structural characteristics and activation mechanism of an RTK. RTKs are transmembrane glycoproteins that consist of an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular kinase domain. They are activated by ligand binding and then transduce the extracellular signal to the cytoplasm by phosphorylating tyrosine residues on the receptors themselves (autophosphorylation) and on downstream signaling proteins.