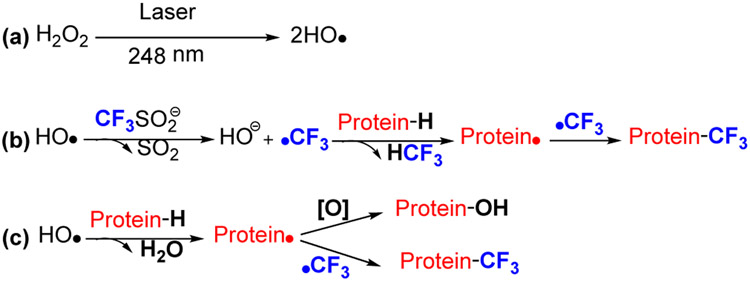
Figure 11.
Mechanism of radical trifluoromethylation. •OH is formed by laser photolysis of HO-OH (pathway a), followed by •OH oxidation of CF3SO2− to form the reactive intermediate CF3SO2•, which generates •CF3 via entropy-driven loss of SO2. The electron-deficient •CF3 readily adds to proteins (pathway b). In alternatively minor pathway c, HO• directly abstracts H• from the protein to produce a protein radical that either couples with •CF3 to provide a CF3-modified product or reacts with HO• to generate oxygen-containing products.