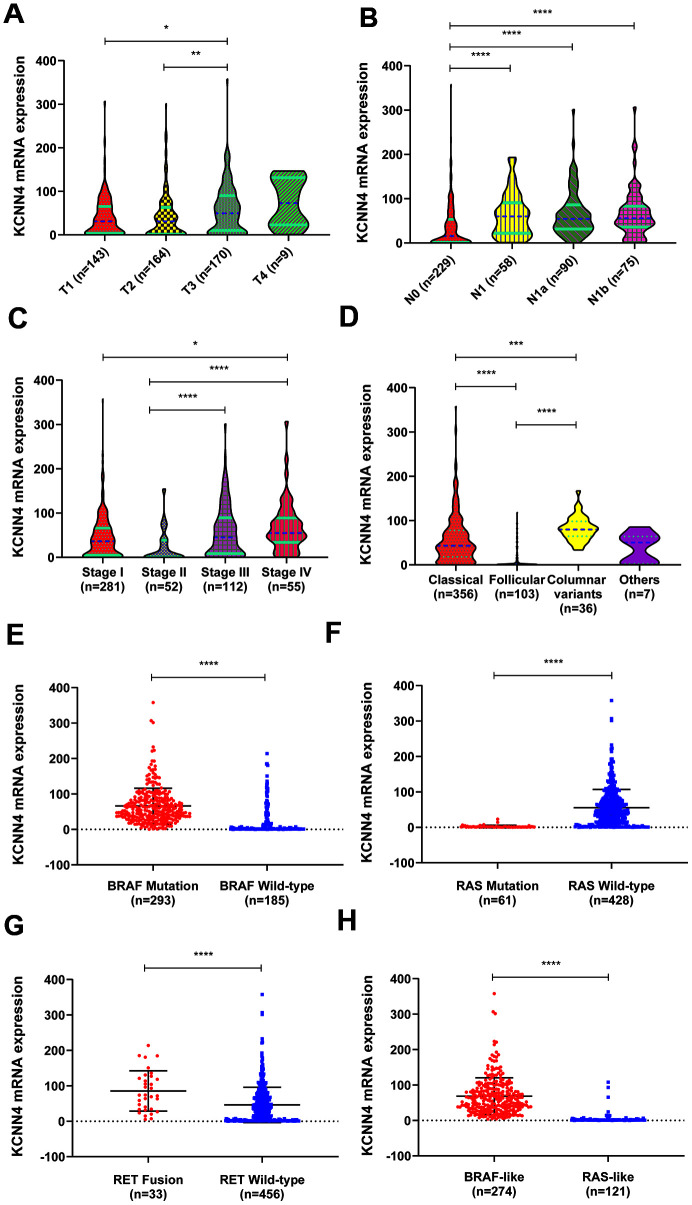
Figure 3.
The relationship between KCNN4 expression and clinicopathological characteristics of PTC. (A–C) KCNN4 expression varied according to the T stage, N stage and tumor stage. Higher KCNN4 expression tended to be associated with worse clinicopathological features. (D) The expression of KCNN4 in different subtypes of PTC. KCNN4 was significantly upregulated in the columnar variant subtype and the classical subtype compared to the follicular subtype. (E) KCNN4 expression was significantly higher in the BRAF mutation group than in the BRAF wild-type group. (F) KCNN4 expression was significantly higher in the RAS wild-type group than in the RAS mutation group. (G) KCNN4 expression was significantly higher in the RET fusion group than in the RET wild-type group. (H) KCNN4 expression was higher in the BRAF-like group than in the RAS-like group. Statistical analyses were performed as follows: A-D: Kruskal-Wallis test; E-H: Mann-Whitney test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.