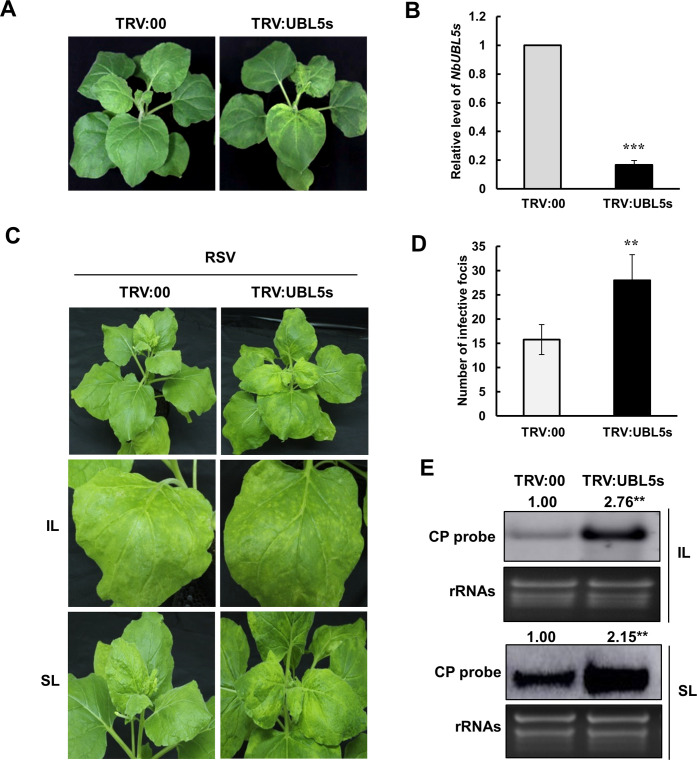
Fig 2. Silencing of NbUBL5s facilitates the infection of RSV.
A. Silencing of NbUBL5s caused chlorosis on the top leaves but had no other effects on plant development. B. qRT-PCR revealed that the expression of NbUBL5s in TRV:UBL5s-infected plants was decreased to 20% of that in the control plants treated with TRV:00, indicating the silencing of NbUBL5s. C. RSV infection was monitored on NbUBL5s-silenced plants. At 7 dpi of RSV inoculation, NbUBL5s-silenced plants had more yellow infection foci and higher levels of accumulation of RSV RNAs than controls in their inoculated leaves. At 20 dpi, RSV-systemically infected leaves showed typical RSV symptoms in both TRV:00-infected and TRV:UBL5s-infected plants. D. The numbers of infection foci on the inoculated leaves of plants. E. Northern blot analysis showed that RSV RNAs in NbUBL5s-silenced leaves accumulated at higher levels than in controls. RSV CP probe was used for analysis. IL: inoculated leaves. SL: systemically infected leaves. Results are from three independent repeats. Twenty plants were used for each repeat. Bars represent the standard errors of the means from three biological repeats. Band intensity in blots was calculated by ImageJ based on three replicates. A two-sample unequal variance directional t test was used to test the significance of the difference (**, p value<0.01; ***, p value<0.001).