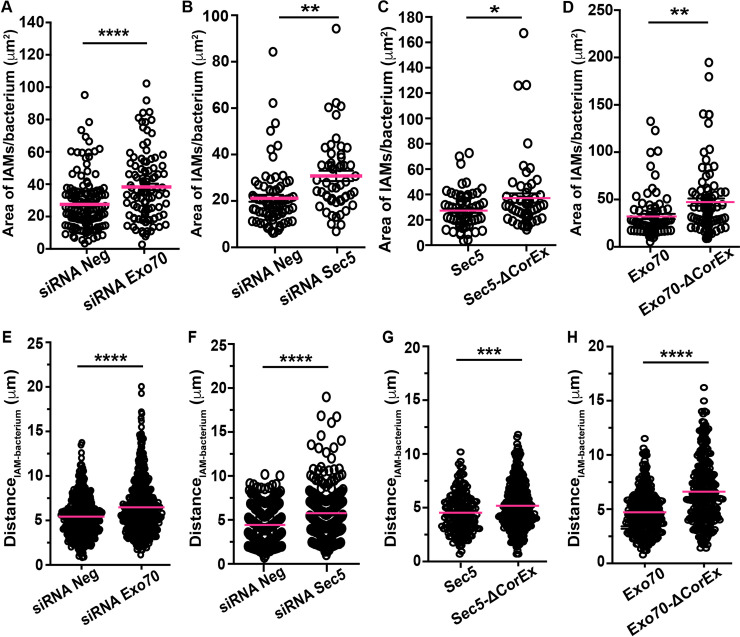
Fig 3. The exocyst is required for tethering IAMs to the S. flexneri-containing vacuole.
S. flexneri infection of HeLa cells was performed in different conditions in the presence of fluorescent dextran, after which the areas occupied by the S. flexneri IAMs and the distances between individual IAMs and S. flexneri were quantified and compared in (A, E) cells subjected to RNA interference of non-targeting control (siRNA Neg) versus Exo70 depletion (siRNA Exo70), (B, F) cells subjected to RNA interference of non-targeting control (siRNA Neg) versus Sec5 depletion (siRNA Sec5) (C, G) cells expressing wild-type Sec5 versus cells expressing Sec5 lacking the core exocyst assembly motif (Sec5-ΔCorEx) and (D, H) cells expressing wild-type Exo70 versus cells expressing Exo70 lacking the core exocyst assembly motif (Exo70-ΔCorEx). At least a total of 55 infections foci were analyzed in triplicate experiments for each condition (n > 55). The bars (magenta) represent the mean and unpaired t-tests were carried out (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001).