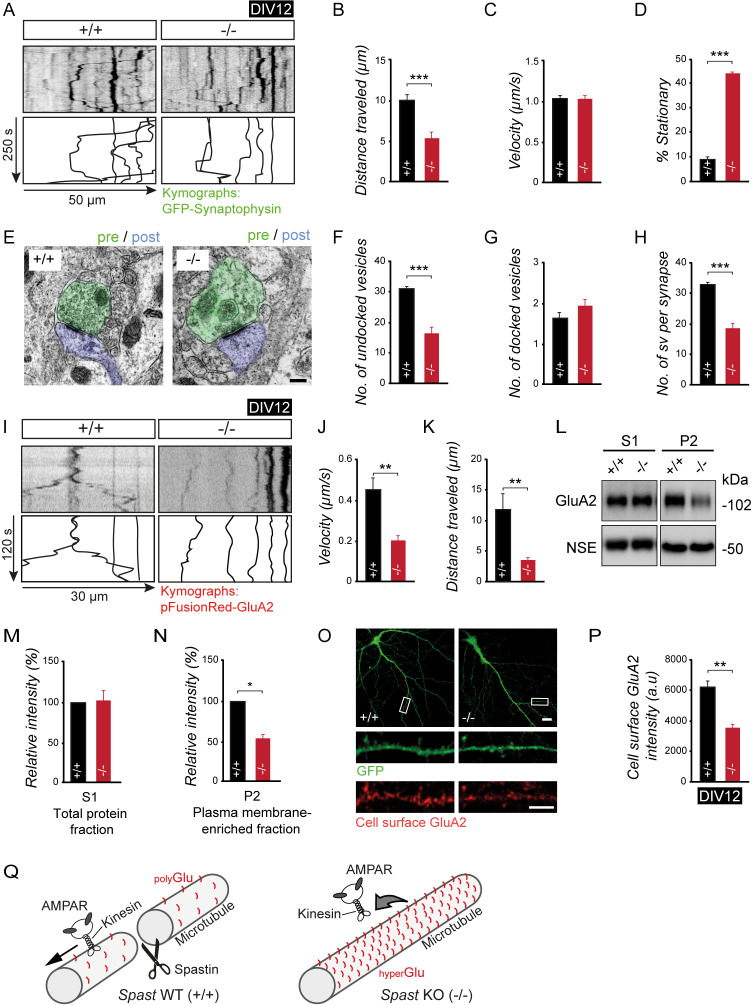
Fig 7. Spastin depletion impairs synaptic cargo transport and cell surface delivery.
(A-D) Live imaging of Synaptophysin-EGFP transport. (A) Kymograph. (B) Travel distance. (C) Velocity. (D) Percent of stationary particles in axons. (+/+) n = 152 (15 cells), (−/−) n = 130 (12 cells). Images were taken at one frame per second. (E-H) Presynaptic vesicle analysis using EM. (E) Electron micrograph from CA1. Scale bar, 200 nm. (F) Undocked vesicle number. (G) Docked vesicle number. (H) Vesicles per synapse terminal. (+/+) n = 3 mice, (−/−) n = 3 mice. Student t test was used to assess statistical significance. (I-K) AMPAR neuronal transport detecting pFusionRed-GluA2 particle mobility over time. (I) Kymograph. (J) Velocity. (K) Travel distance. (+/+), n = 17 (12 cells) particles; (−/−), n = 16 (12 cells). (L-N) GluA2 subcellular expression levels analyzed using western blotting, following subcellular fractionation. (L) Representative western blots. (M) Quantification of GluA2 in total protein fraction (S1). (+/+), n = 7; (−/−), n = 6. (N) Quantification of GluA2 in plasma membrane–enriched fraction (P2). (+/+) n = 4, (−/−) n = 4. NSE used as loading control. (O, P) GluA2-AMPAR cell surface staining using DIV18 neurons. (O) Cell surface GluA2 (red) expression in dendrites; scale bar, 10 μm; magnification, 5 μm. EGFP (green) used as volume marker. (P) Cell surface GluA2 signal intensity. (+/+), n = 19; (−/−), n = 19. Student t test was used to assess statistical significance. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are represented as means ± SEM. (Q) Model. Loss of spastin-mediated MT severing leads to longer MTs characterized by an accumulation of tubulin polyglutamyl side chains. The resulting increase in negative charge at the MT surface affects the binding and mobility of motors (e.g., kinesins) and their respective cargo proteins (e.g., vesicular AMPARs). The observed deficits in synaptic cargo delivery are in agreement with the cognitive deficits in spastin KO mice and patients with SPG4-type HSP. Individual quantitative observations that underlie the data presented in this figure are summarized in S7 Data. AMPAR, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor; DIV, days in vitro; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; EM, electron microscopy; GluA2, Glutamate receptor AMPA type subunit 2; KO, knockout; MT, microtubule; NSE, neuron specific enolase; SPG, spastic paraplegia.