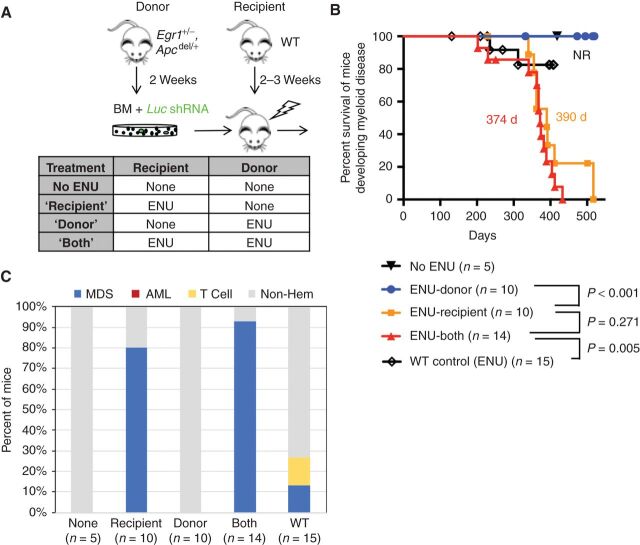
Figure 5.
ENU exposure of the BM microenvironment is a major force driving MDS development in mice transplanted with Egr1 and Apc haploinsufficient HSPCs. A, Schematic of the transplantation schemes used to elucidate the effects of alkylating agents on HSPCs (donor) versus the microenvironment (recipient) in the absence of Trp53 knockdown. WT recipients were transplanted with Egr1+/−, Apcdel/+ BM cells transduced with Luc shRNA (control) under 4 different ENU conditions. Donor mice received one injection of ENU (100 mg/kg) 2 weeks before bone marrow harvest. Recipient mice received one injection of ENU (100 mg/kg) 3 weeks before lethal irradiation and transplantation. B, Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice developing myeloid disease. Survival time is similar when only recipient mice are exposed (390 days) versus when both donor and recipient mice are exposed to ENU (374 days; P = 0.271). As a control, WT BM was transplanted into WT recipients, and then treated with ENU; median survival was not reached as only 2 of 15 (13%) mice developed MDS. C, Histologic classification of diseases arising in the mice. The percent of mice that developed MDS in ENU-recipient (80%) and ENU-both (93%) conditions was similar (P = 0.55 by Fisher exact test).