Fig. 5. T. amphioxeia morphology.
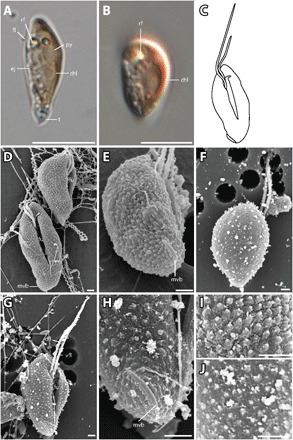
(A) Lateral view of elongated T. amphioxeia cell with olive-brown color with chloroplast, refractosome (rf), pyrenoid, and ejectosomes. (B) Lateral view of a more round T. amphioxeia cell, more reddish in color with chloroplast and refractosome. (C) Drawing of T. amphioxeia surface characters. (D) Ventral and lateral view of cells with intact SPC with a papillate structure (fixation with Lugol’s solution), furrow, and mid-ventral band that is almost lateral at the antapical end. (E) View from lateroposterior on the cell with SPC showing the short mid-ventral band. (F) Dorsal view of the cell with sheet-like IPC (fixation with OsO4). (G) Ventral view showing the furrow and ventral flagellum that is longer than the dorsal flagellum. (H) Detail of the antapical end with the mid-ventral band, which is short and curved and does not extend to the furrow. (I) Detail of the cell surface SPC visible in fixation with Lugol’s solution. (J) Detail of the cell surface IPC in fixation with OsO4. Scale bars are 10 μm (light microscopy) and 1 μm (SEM). Anterior of all cell oriented upwards.
