Figure 4. Interactions and functional implications of EDF1 and Mbf1.
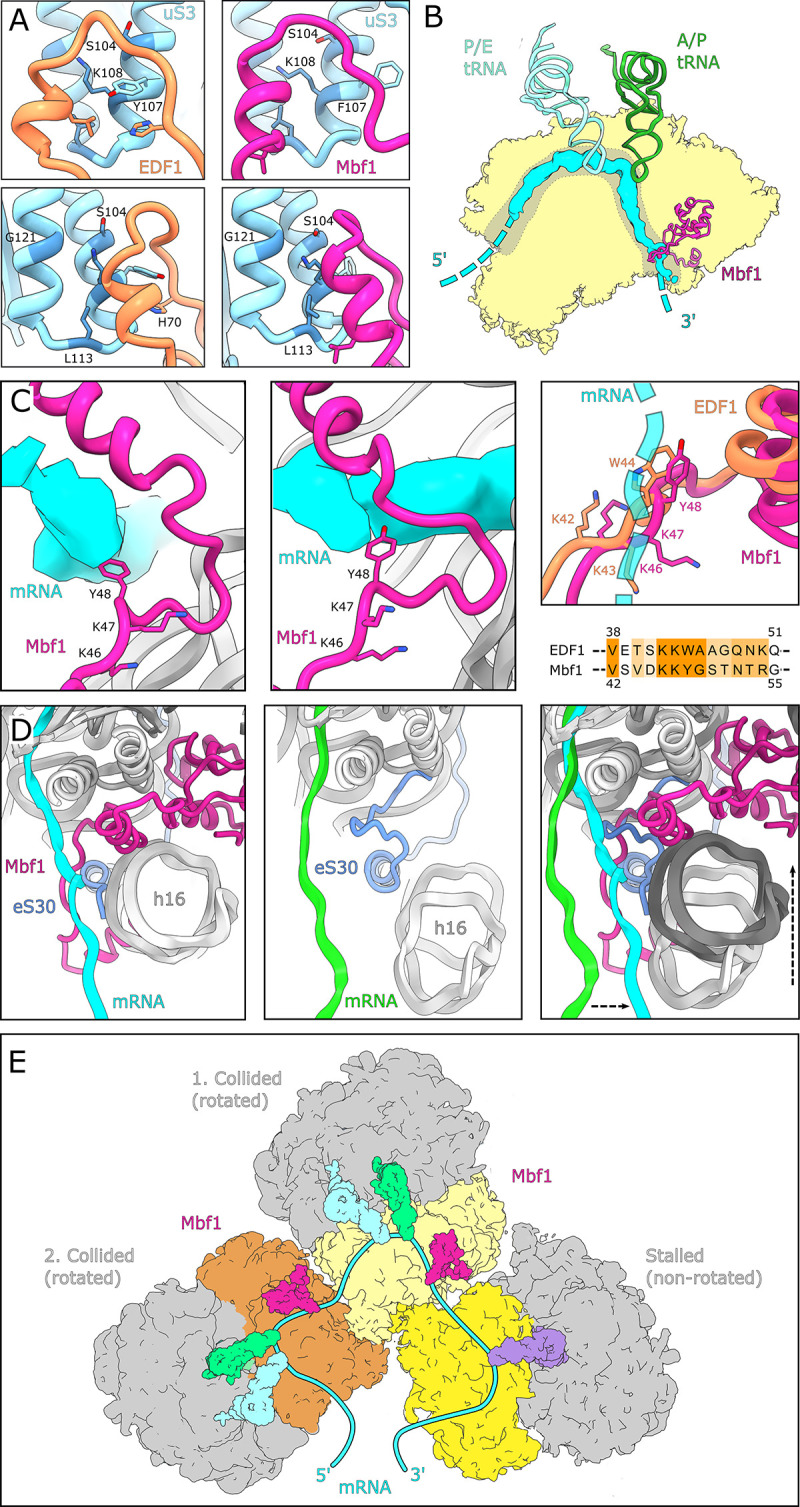
(A) EDF1 (orange) and Mbf1 (violet red) interact with ribosomal protein uS3 via a helix-helix interaction. In the human structure, Y107 of uS3 is stacks with H70 of EDF1. Conserved residues required for frameshift inhibition in yeast are colored in steel blue. (B) Overview of Mbf1’s position with respect to the mRNA path on the 40S ribosomal subunit. (C) Mbf1 clamps the mRNA into a headlock, with the aromatic amino acid Y48 exposed to facilitate interaction with the mRNA. The KKY-motif is well conserved between Mbf1 and EDF1 (KKW). (D) Comparison of the mRNA path of a Mbf1-bound colliding ribosome with that of a canonical colliding ribosome (PDB: 6I7O). The mRNA and helix 16 are shifted in Mbf1-bound ribosomes. (E) Overview of the Mbf1-ribosome interaction in collided polysomes. Mbf1 binds the second and third ribosomes of the trisome unit.
