Figure 6.
Adenovirus-Mediated Deletion of miR-126 Suppresses the Proliferation and Differentiation of SOX9+ LPCs to Aggravate Liver Damage through Hoxb6 in a CCl4 Chronic Injury Model
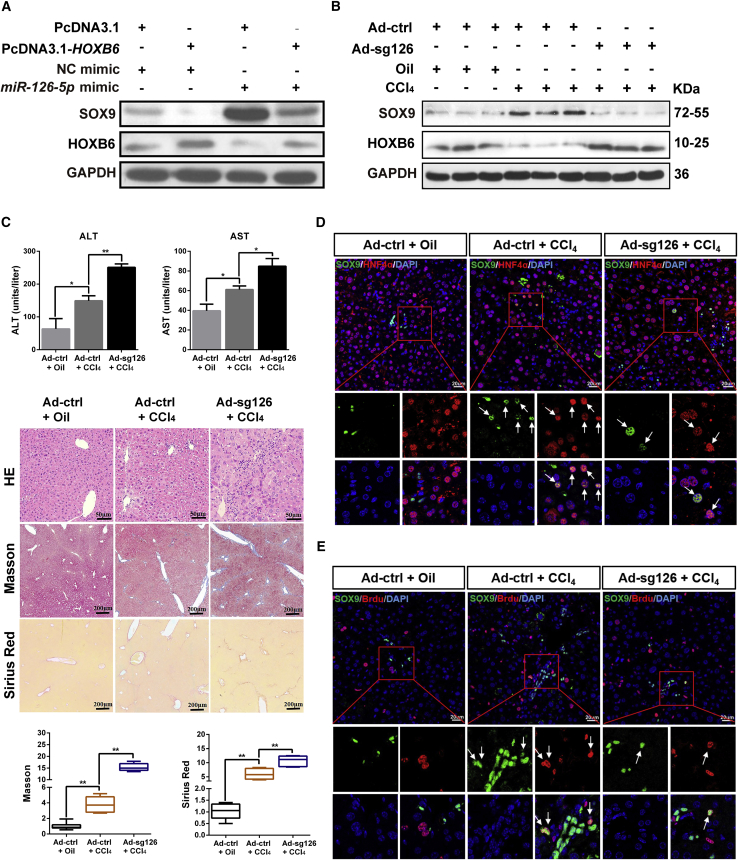
(A) PcDNA3.1 or PcDNA3.1-HOXB6 was co-transfected with miR-126-5p mimics or NC into HepG2 cells, respectively. HOXB6 and SOX9 levels were measured by western blotting.
(B) Hepatic expression levels of SOX9 and HOXB6 were measured by western blot in CCl4-injured mice following CRISPR/Cas9-mediated miR-126 gene disruption.
(C) Hepatotoxicity and ALT/AST enzymes activities change in CCl4-injured mice following miR-126 gene disruption. Representative H&E, Masson, and Sirius red staining in Ad-ctrl- and Ad-sg126-treated mice liver after chronic hepatic injury by CCl4. Fibrosis was quantified by morphometric measurement of Masson and Sirius red.
(D) SOX9 and HNF4α double staining in periportal areas in livers of Ad-ctrl- or Ad-sg126-treated mice after CCl4 injury. Blue (DAPI) shows nuclei. Red (HNF4α) marks hepatocytes. Green presents SOX9. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
(E) SOX9 and BrdU double staining in periportal areas in livers of Ad-ctrl- or Ad-sg126-treated mice after CCl4 injury. Blue (DAPI) shows nuclei. Red (BrdU) marks the proliferating cells. Green presents SOX9. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
Data are expressed as means ± SD, n = 6 mice per group containing three replicates. Significant difference is presented at the levels of ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 by two-tailed Student's t test. See also Figure S5.