Figure 1.
Distinct Composition and In Vitro Behavior of Myogenic Cells of the CD34+ITGA7+ Fraction of Postnatal or Adult Muscles
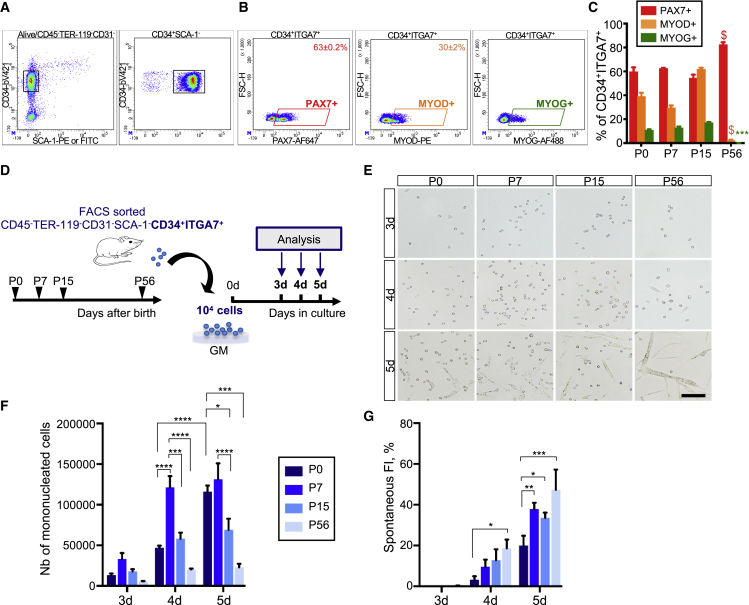
(A and B) Representative density scatterplots showing the gating strategy used to determine the proportion of PAX7+, MYOD+, and MYOG+ cells among the CD45−TER-119−CD31−SCA-1−CD34+ITGA7+ fraction (referred to as CD34+ITGA7+ fraction) from P7 mouse muscles. (A) Debris, doublets, CD45+TER-119+CD31+, and dead cells were excluded from the analysis (Figure S1; Table S1) and ITGA7+ cells were gated from the CD34+SCA-1− fraction. (B) Gates used to determine the proportion of PAX7+, MYOD+, and MYOG+ cells.
(C) Bar graph showing the proportion of PAX7+, MYOD+, and MYOG+ cells. Two-way ANOVA analysis, with ∗∗∗p < 0.001, $p < 0.0001 relative to P0.
(D) Purified CD34+ITGA7+ cells were plated at the same density and cultured in growth medium for 3, 4, and 5 days.
(E–F) (E) Optical micrographs of cultured-myogenic cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. Quantification of (F) the total number of mononucleated cells, (G) their spontaneous fusion index, calculated as number of nuclei incorporated in myotubes on total number of nuclei per field. Values are represented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3 mice/group). Two-way ANOVA analysis, with ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.