Extended data Fig. 10 |. Detailed model illustrating how nucleolar RNA Pol II-dependent R-loops shield the IGS from sincRNA synthesis by Pol I.
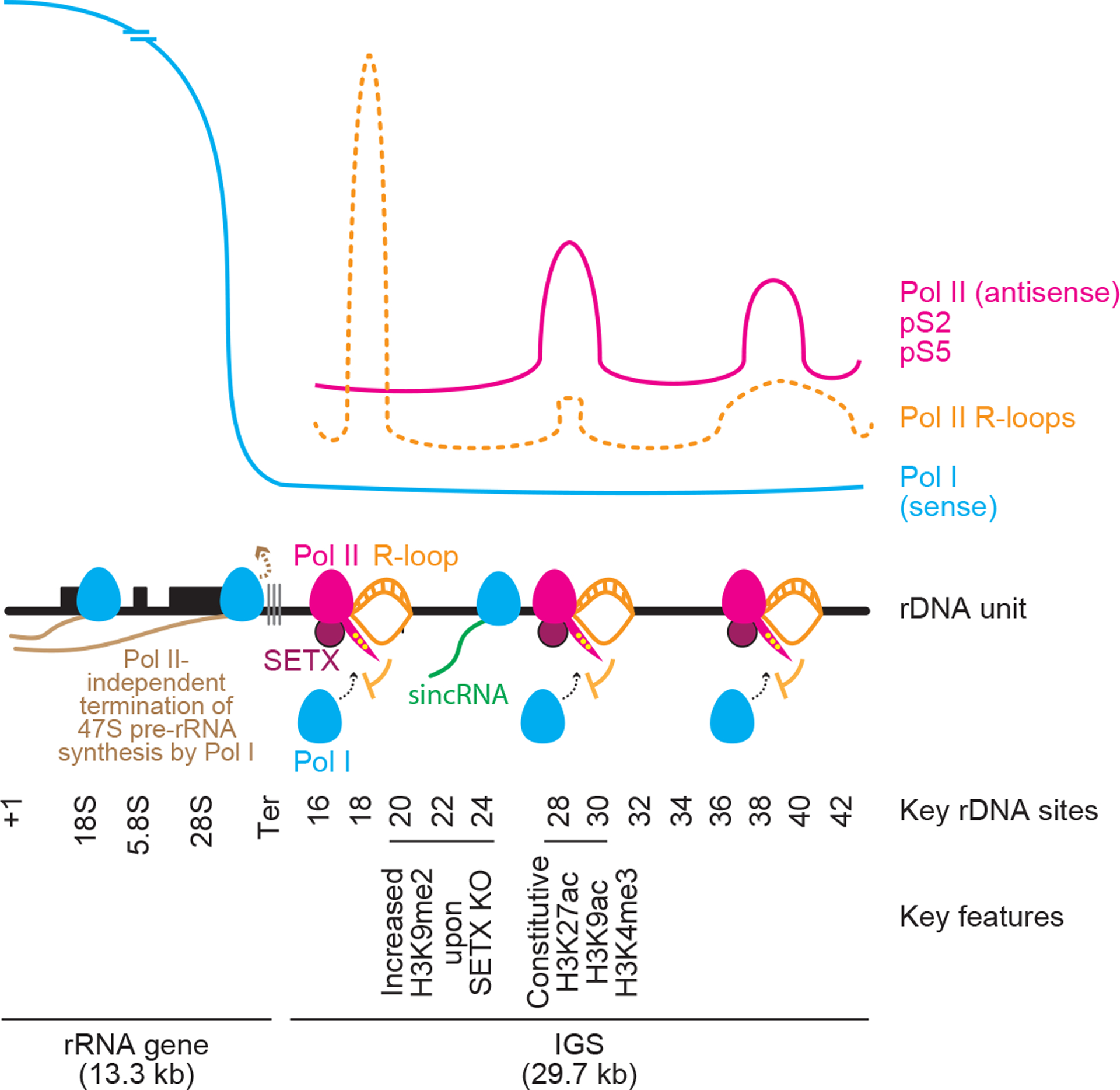
RNA Pol II at rDNA intergenic spacers (IGSs) synthesizes antisense intergenic ncRNAs (asincRNAs) that constitutively engage in DNA-RNA hybrid-containing R-loops. Nucleolar RNA Pol II function is promoted by the neurodegeneration-linked SETX. Disruption of nucleolar Pol II enables the recruitment of RNA Pol I to the IGS. There, Pol I synthesizes sense intergenic ncRNAs (sincRNAs) that mimic environmental stress, disrupting nucleolar liquid-liquid phase separation and triggering aberrant nucleolar liquid-to-solid phase transition. This unscheduled activation of nucleolar stress responses compromises the natural organization of nucleoli, leading to defects in pre-rRNA biogenesis, especially at the processing level. Nucleolar sincRNA levels are naturally elevated in Ewing sarcoma cells, explaining the indistinct nucleoli often seen in this cancer. In the context of Pol II inhibition, SETX loss, or Ewing sarcoma, sincRNA repression ameliorates nucleolar organization and rRNA biogenesis.
