Fig. 3. Repression of an IGS R-loop shield disrupts nucleoli.
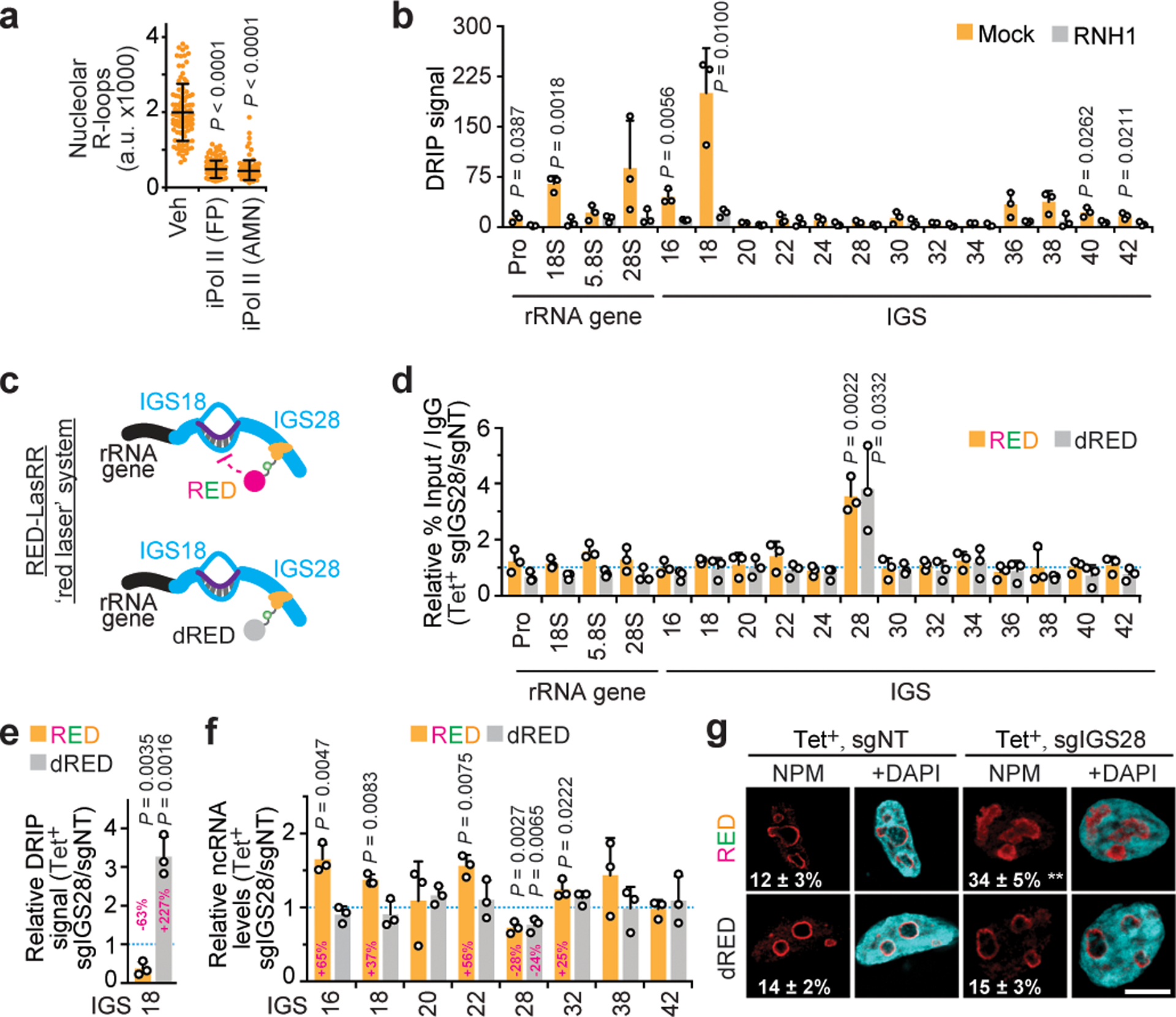
(a) Pol II inhibition repressed nucleolar R-loops. (b) DRIP showing RNase H1-sensitive R-loop peaks at rDNA. (c) The RED-LasRR system created to achieve inducible locus-associated R-loop repression. (d) The short guide RNA for IGS28 (sgIGS28) enriched RED or dRED at IGS28 in anti-GFP ChIP. Enrichments are normalized to a non-targeting control (sgNT). RED and dRED data were from different experiments but are shown on the same graph as a space-saving measure. (e) Using RED or dRED together with sgIGS28 decreased and increased R-loop levels at IGS18, respectively. (f,g) RED sgIGS28 induced ncRNA levels (f) and disrupted NPM localization (g). The percentage of cells exhibiting ruffled NPM localization is indicated on images (g). (a-g) HEK293 cells; data are shown as the mean±s.d.; two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test, n=100 cells (a), or two-tailed t-test, n=3 biologically independent experiments (b, d-f); scale bar, 5 μm. Percent changes relative to respective sgNT samples are indicated above or onto bars (e-f).
