Extended data Fig. 1 |. Additional characterization of Pol I and Pol II occupancies at rDNA IGSs.
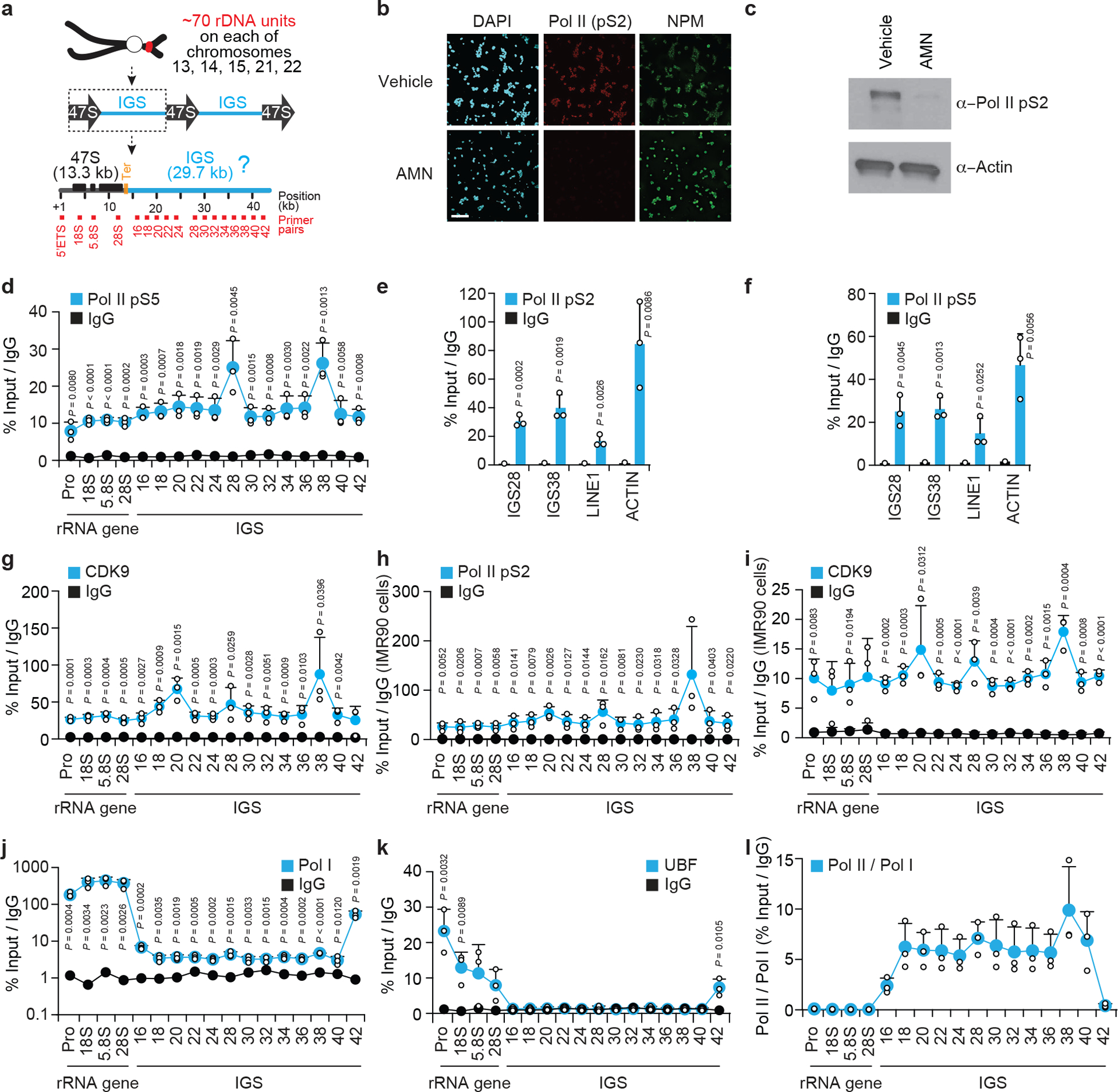
(a) Organization of human rDNA repeats. At each rDNA unit, Pol I transcribes an rRNA gene encoding a 47S pre-rRNA that is processed to remove transcribed spacers, such as the 5’ ETS, and generate 18S, 5.8S, and 28S rRNA molecules. The IGS constitutes the bulk of each rDNA unit. (b-c) Specificity controls indicating that targeting Pol II for degradation with a 12 h α-amanitin treatment does lower anti-Pol II (pS2) signals in both immunofluorescence (b) and immunoblotting (c). For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1. (d) ChIP showing Pol II-pS5 enrichment across rDNA. (e-f) The enrichment of active Pol II forms at rDNA IGS sites is higher than at LINE1 but lower than at β-ACTIN. (g-k) ChIP experiments showing the enrichment of indicated proteins across rDNA. (l) Comparison of the enrichment of RNA Pol II and Pol I across rDNA reveals the relative overrepresentation of Pol II across IGSs only. (b-l) HEK293 (b-g,j-l) or IMR90 (h,i) cells were used; data are shown as the mean±s.d.; two-tailed t-test, n=3 biologically independent experiments (d-l); images in (b-c) are representative of two independent experiments. Data in (d-f,j-l) and Fig. 1b were from large experimental sets sharing IgG controls. Data in (h,i) were from large experimental sets sharing IgG controls.
